OIDC authentication with JumpCloud EARLY ACCESS
This section describes how to configure a YugabyteDB Anywhere (YBA) universe to use OIDC-based authentication for YugabyteDB YSQL database access using JumpCloud as the Identity Provider (IdP).
After OIDC is set up, users can sign in to the YugabyteDB universe database using their JSON Web Token (JWT) as their password.
Note that the yugabyte privileged user will continue to exist as a local database user even after OIDC-based authentication is enabled for a universe.
Learn more
Set up OIDC with JumpCloud on YugabyteDB Anywhere
To enable OIDC authentication with JumpCloud, you need to do the following:
- Create an app registration in JumpCloud - The JumpCloud IdP configuration includes application registration (registering YugabyteDB Anywhere in the JumpCloud tenant) and configuring JumpCloud to send (redirect) tokens with the required claims to YugabyteDB Anywhere.
- Configure OIDC in YugabyteDB Anywhere - The OIDC configuration uses the application you registered. You can also configure YBA to display the user's JSON Web Token (JWT) on the sign in screen.
- Configure the universe to use OIDC - You enable OIDC for universes by setting authentication rules for database access using flags. The database is implicitly configured and picks up the authentication rules you set. The database uses well-known PostgreSQL constructs to translate these authentication rules into database roles for access. Mapping JumpCloud attributes, such as group memberships, roles, and email addresses to database roles, is accomplished using the PostgreSQL
yb_hba.confandyb_ident.conffiles.
Create an application in JumpCloud
To use JumpCloud for your IdP, do the following:
-
Sign in to JumpCloud using an administrator account.
-
Create an application.
- Under SSO Applications, click Add New Application.
- Select Custom Application, and make sure the integration supports "SSO with OIDC" on the next page.
- Under Manage Single Sign-On (SSO), select Configure SSO with OIDC, and click Next.
- Under Enter General Info, add the application name (for Display Label), Description, and logo (for User Portal Image), and select Show this application in User Portal.
- Click Configure Application.
-
Configure your application.
Under SSO > Endpoint Configuration, configure the following:
- Redirect URIs - enter
https://<your-YugabyteDB-Anywhere-IP-address>/api/v1/callback?client_name=OidcClient. - Client Authentication Type - select Client Secret Post.
- Login URL - enter
https://<your-YugabyteDB-Anywhere-IP-address>/login.
Under Attribute Mapping, for Standard Scopes, select Email and Profile.
Click Activate when you are done.
You will be prompted in a pop up to save the Client ID and Client Secret. Save these in a secure location, you will need to provide these credentials in YugabyteDB Anywhere.
- Redirect URIs - enter
-
Configure Attributes and Identity Management as required.
-
Integrate the user in JumpCloud.
- Navigate to User Groups, select the user groups you want to access YugabyteDB Anywhere, and click Save when you are done.
To configure JumpCloud federated authentication in YugabyteDB Anywhere, you need the following application properties:
- Client ID and Client Secret of the application you created. These are the credentials you saved when you activated your application. The Client ID is also displayed on the SSO tab.
For more information, refer to the JumpCloud documentation.
Configure YugabyteDB Anywhere
To configure YugabyteDB Anywhere for OIDC, you need to be signed in as a Super Admin. You need your JumpCloud application client ID and client secret.
To allow users to access their JWT from the YugabyteDB sign in page, you must enable the OIDC feature via a configuration flag before you configure OIDC.
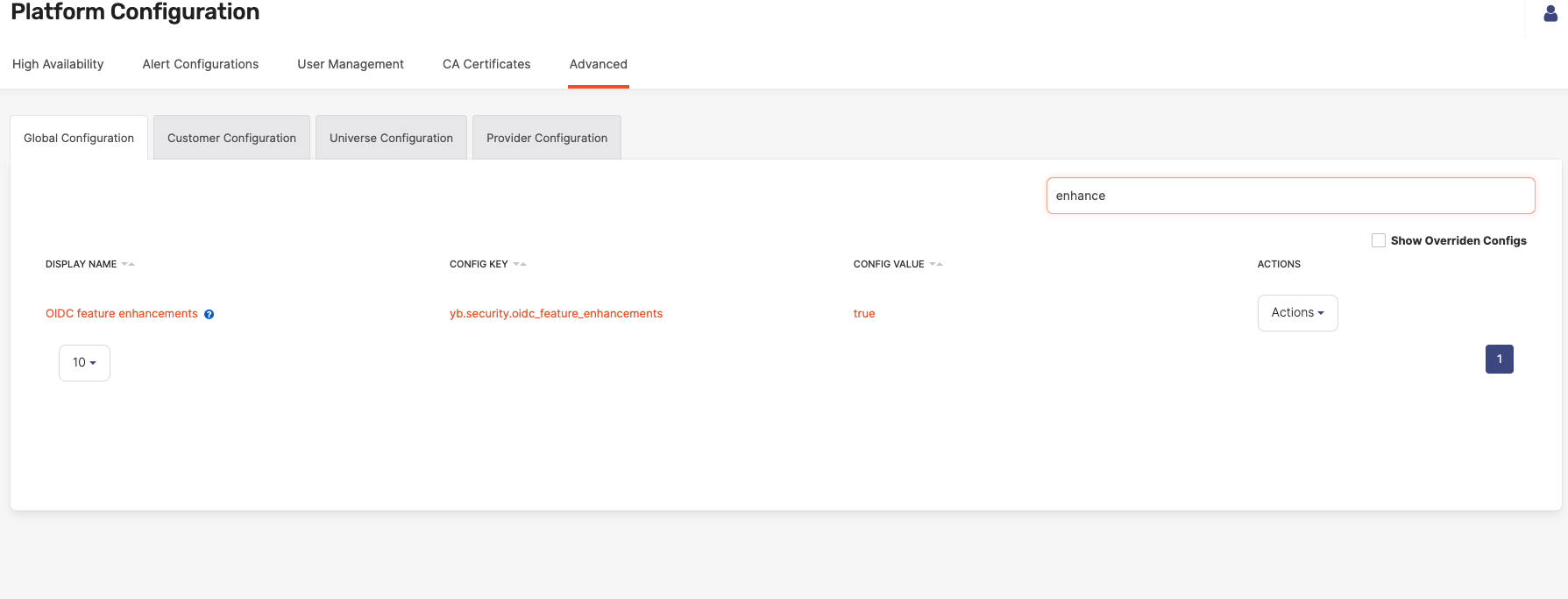
Enable OIDC enhancements
To enable some features of the OIDC functionality in Yugabyte Anywhere, you need to set the yb.security.oidc_feature_enhancements configuration flag to true as follows:
-
Navigate to Admin > Advanced > Global Configuration.
-
Search on OIDC to display the configuration setting and set it to true.
Enable OIDC authentication
To configure User authentication in YugabyteDB Anywhere, do the following:
-
Navigate to Admin > Access Management > User Authentication and select ODIC configuration.
-
Under OIDC configuration, configure the following:
- Client ID and Client Secret - enter the client ID and secret of the JumpCloud application you created.
- Discovery URL - enter
https://oauth.id.jumpcloud.com/.well-known/openid-configuration. - Scope - enter
openid email. If you are using the Refresh Token feature to allow the Jumpcloud server to return the refresh token (which can be used by YBA to refresh the login), enteropenid offline_access profile emailinstead. - Email attribute - enter your registered email.
- Refresh Token URL - if you have configured OIDC to use refresh tokens, in the Refresh Token URL field, enter the URL of the refresh token endpoint.
- Display JWT token on login - select this option to allow users to access their JWT from the YugabyteDB Anywhere sign in page. This allows a user to view and copy their JWT without signing in to YBA. (This option is only available if you enabled the
yb.security.oidc_feature_enhancementsconfiguration flag.)
-
Click Save.
You are redirected to sign in to your IdP to test the connection. After the test connection is successful, OIDC authentication is enabled.
Configure a universe
To access a universe via OIDC, you need to set the following flags on the universe:
- ysql_hba_conf_csv
- ysql_ident_conf_csv
When the flags are set, YugabyteDB configures the ysql_hba.conf and yb_ident.conf files on the database nodes and creates the files that hold the JWKS keys for token validation.
For information on configuring flags in YugabyteDB Anywhere, refer to Edit configuration flags.
ysql_hba_conf_csv
The ysql_hba_conf_csv flag must be set to support using JWTs for authentication. The parameters to include in the configuration file record are as follows:
jwt_map- the user-name map used to translate claim values to database roles. Optional if you aren't using the default Subject claim values.jwt_issuers- the first part of the discovery URL (https://oauth.id.jumpcloud.com/)jwt_audiences- the audience or target app for the token, which in this case is the client ID of the application you registered.jwt_matching_claim_key- the email attribute you set (for example,preferred_username). Optional if you aren't using the default Subject claim values.jwt_jwks_path- The JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) is a set of keys containing the public keys used to verify any JWT. These can be uploaded as entries in a single file. When configuring the flag in YugabyteDB Anywhere, click Add JSON web key set (JWKS) to upload the JWKS.
The following illustration shows an example of setting the ysql_hba_conf_csv flag in YugabyteDB Anywhere:
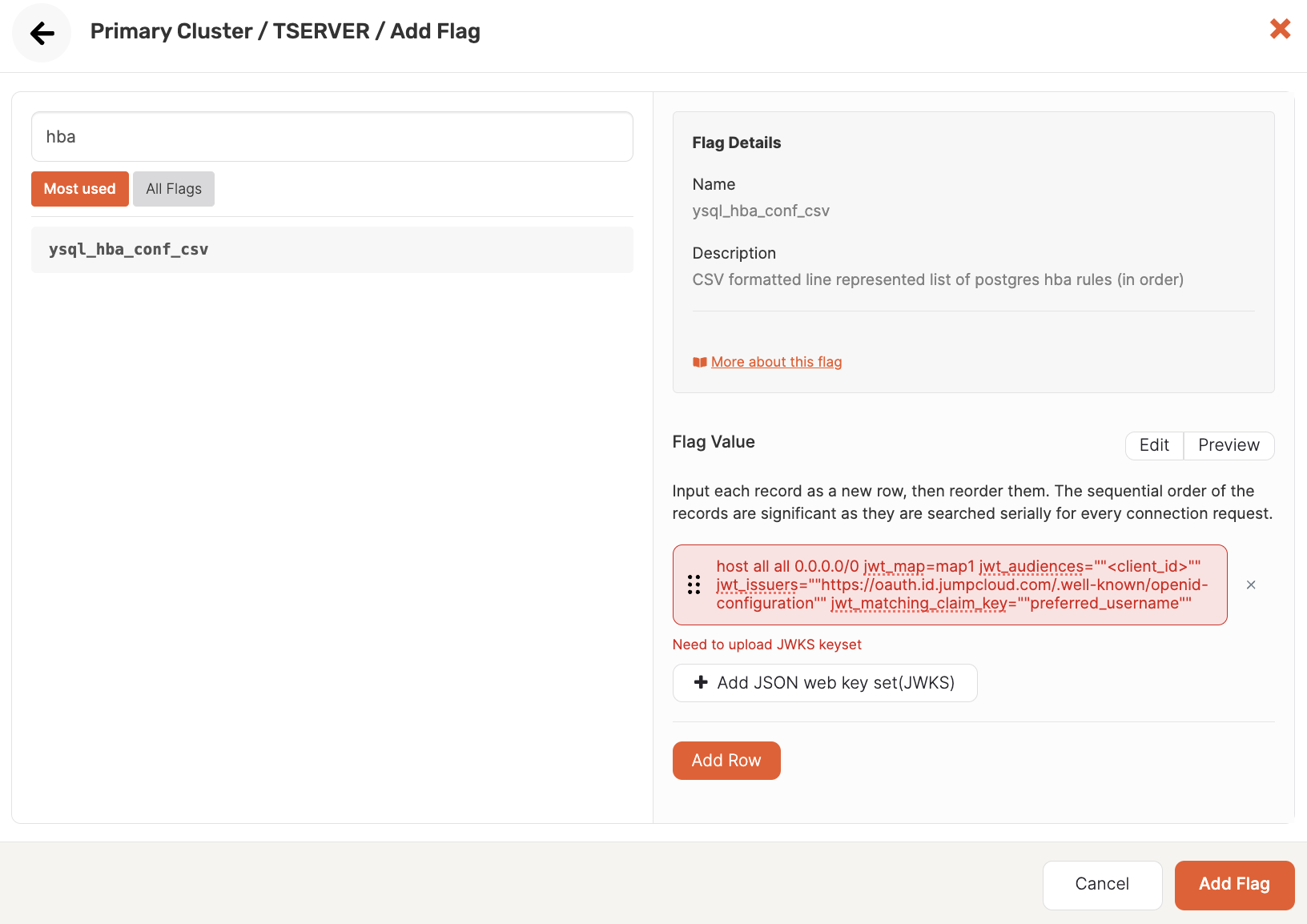
The following shows an example ysql_hba_conf_csv flag configuration for OIDC:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 jwt_map=map1 jwt_audiences=""<client_id>"" jwt_issuers=""https://oauth.id.jumpcloud.com/"" jwt_matching_claim_key=""preferred_username""
For more information on host authentication in YugabyteDB using ysql_hba_conf_csv, refer to Host-based authentication.
ysql_ident_conf_csv
This flag is used to add translation regex rules that map token claim values to PostgreSQL roles. The flag settings are used as records in the yb_ident.conf file as user-name maps. This file is used identically to pg_ident.conf to map external identities to database users. For more information, refer to User name maps in the PostgreSQL documentation.
The following illustration shows an example flag configuration:
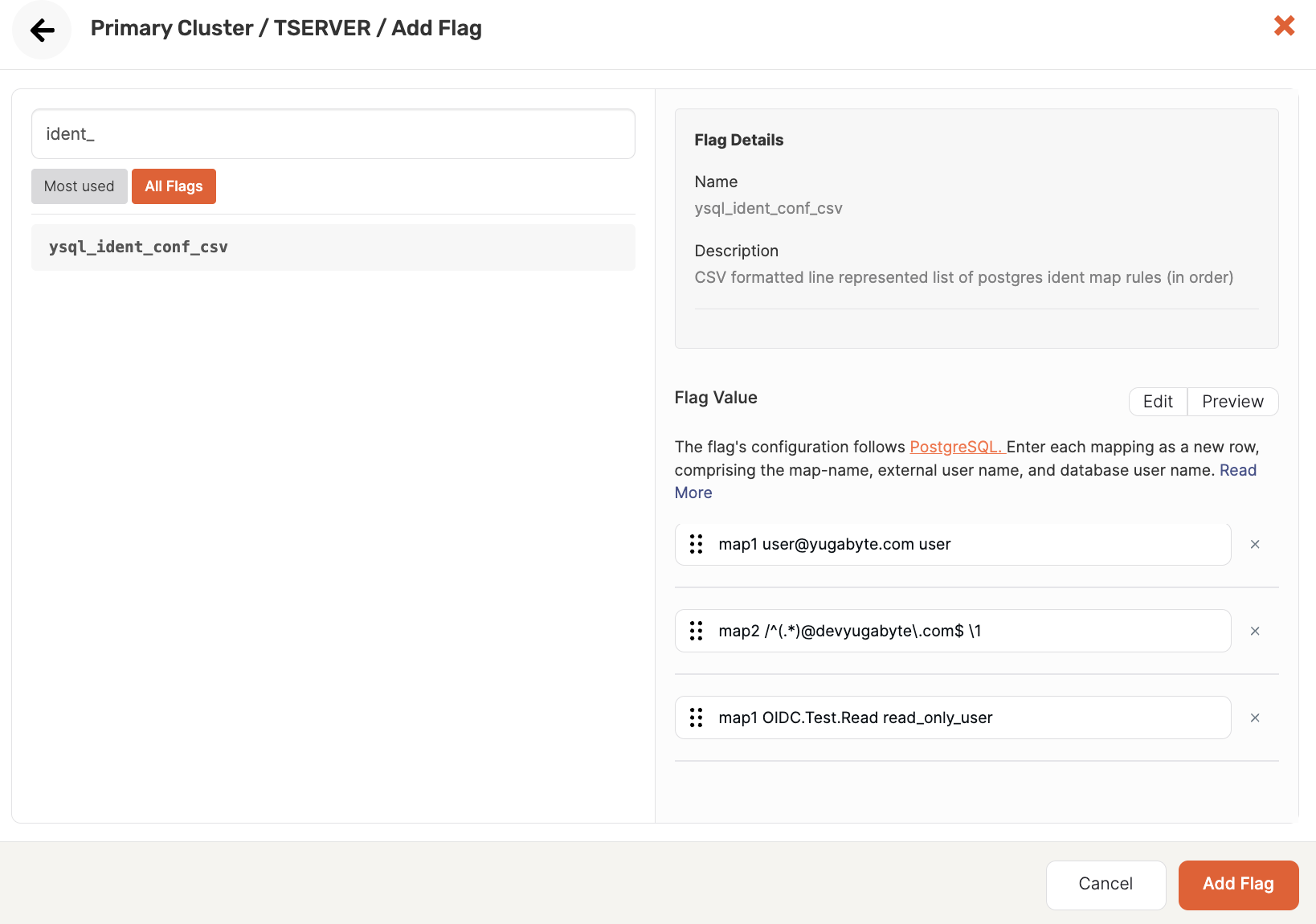
The following are examples of possible rules:
-
Map a single user
map1 user@yugabyte.com user -
Map multiple users
map2 /^(.*)@devyugabyte\.com$ \1 -
Map Roles <-> Users
map1 OIDC.Test.Read read_only_user
yb.security.oidc_feature_enhancements
This flag must be enabled to expose the OIDC functionality in Yugabyte Anywhere. Use the following API to set values for this flag.
curl -k --location --request PUT '<server-address>/api/v1/customers/<customerUUID>/runtime_config/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/key/yb.security.oidc_feature_enhancements' \
--header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'X-AUTH-YW-API-TOKEN: <api-token>' \
--data 'true'
Manage users and roles
After OIDC-based authentication is configured, an administrator can manage users as follows:
-
In the universe, add database users or roles.
You need to add the users and roles that will be used to authenticate to the database. The role must be assigned the appropriate permissions in advance. Users will use their database user/role as their username credential along with their JWT as the password when connecting to the universe.
For information on managing users and roles in YugabyteDB, see Manage users and roles.
-
In YugabyteDB Anywhere, create YBA users.
Create a user in YugabyteDB Anywhere for each user who wishes to sign in to YBA to obtain their JWT.
To view their JWT, YBA users can sign in to YugabyteDB Anywhere, click the User icon at the top right, select User Profile, and click Fetch OIDC Token.
This is not required if you enabled the Display JWT token on login option in the YBA OIDC configuration, as any database user can copy the JWT from the YBA landing page without signing in to YBA.
For information on how to add YBA users, see Create, modify, and delete users.
Using your JWT
If the administrator has enabled the Display JWT token on login setting, you can obtain your token from the YugabyteDB Anywhere landing page. Click Fetch JSON Web Token; you are redirected to the IdP to enter your credentials as required. You are then redirected back to YugabyteDB Anywhere, where your token is displayed, along with the expiration time of the token.
Use the token as your password to access the database. Your username will match the database username/role that was assigned to you by your administrator.