Building applications with Hasura
Use the Hasura GraphQL Engine with YugabyteDB to power your GraphQL applications with a distributed database.
For details on using Hasura, see the Hasura GraphQL engine documentation.
Prerequisites
Before using Hasura with YugabyteDB, perform the following:
-
Install and start YugabyteDB, as described in Quick Start Guide.
-
Install and start Hasura by following instructions provided in the Hasura Quick Start with Docker. The configuration should be similar to PostgreSQL, except that the port should be
5433. For a local Mac setup, the configuration should be as follows:docker run -d -p 8080:8080 \ -e HASURA_GRAPHQL_DATABASE_URL=postgres://postgres:@host.docker.internal:5433/yugabyte \ -e HASURA_GRAPHQL_ENABLE_CONSOLE=true \ hasura/graphql-engine:v1.3.3In the preceding command,
v1.3.3refers to the version ofhasura/graphql-engineyou are using; you can change it to a different version as per your needs.@host.docker.internal:5433is a directive to Hasura to connect to the 5433 port of the host that is running the Hasura container.Alternatively, you can connect YugabyteDB to Hasura Cloud. For more information, see Getting Started with Hasura Cloud.
Examples provided in this document are based on a local installation of Hasura.
Creating tables
You can add tables to the database that you specified in the HASURA_GRAPHQL_DATABASE_URL setting in your Hasura installation. You can also create relationships between these tables. To do this, open Hasura on http://localhost:8080 and perform the following:
-
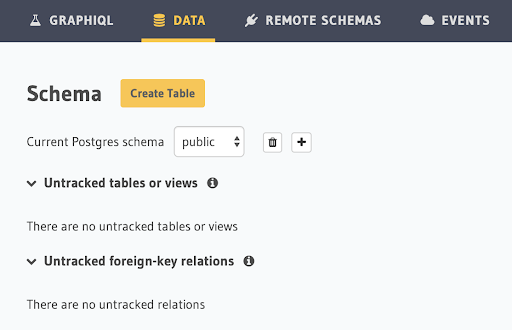
Select DATA and click Create Table, as per the following illustration:
-
Create a table called
authorthat has two columns (idandname) by completing the fields shown in the following illustration: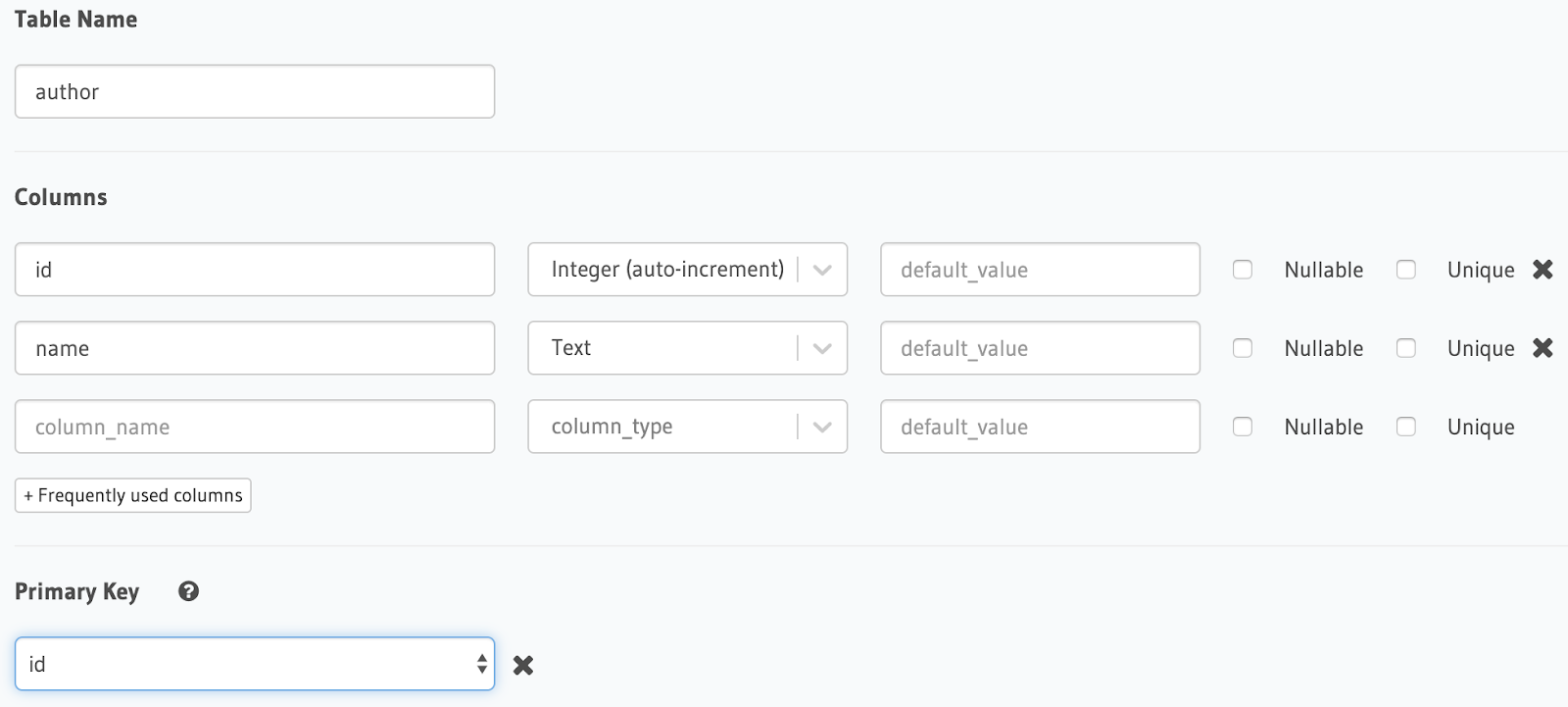
-
Click Add Table.
-
Navigate back to DATA and click Create Table again.
-
Create a table called
articlethat has five columns (id,title,content,rating,author_id) with a foreign key reference to theauthortable, by completing the fields shown in the following illustration: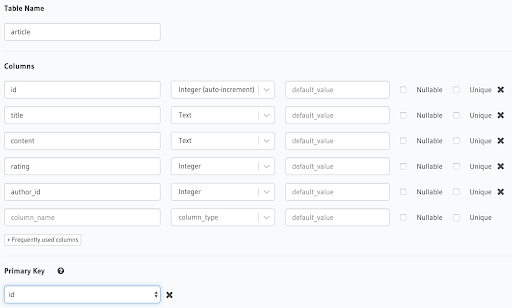
-
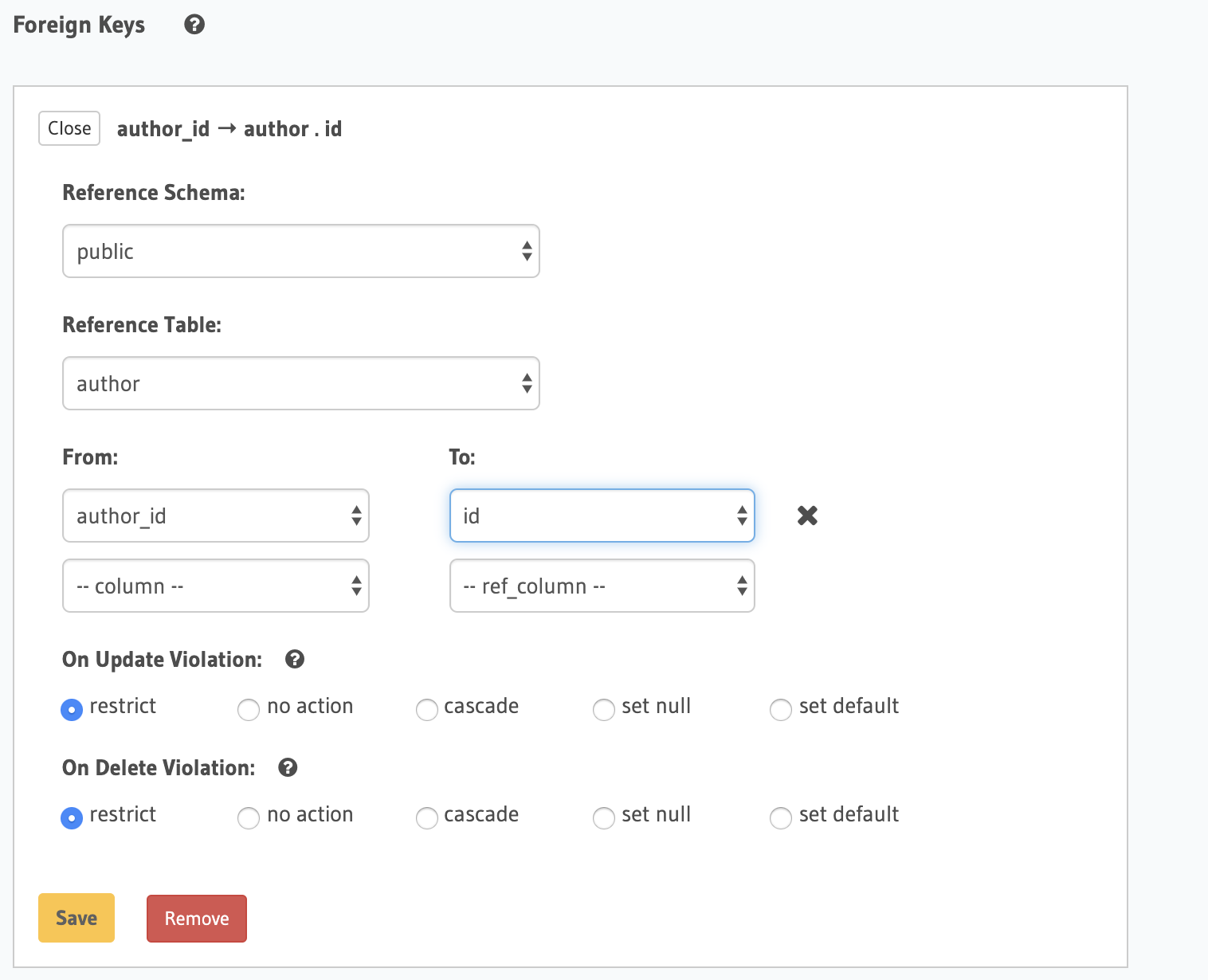
In the Foreign Keys section, click Add a foreign key and complete the fields shown in the following illustration:
-
Click Save on the foreign key configuration.
-
Click Add Table at the bottom.
-
Navigate back to DATA.
-
To create an object relationship, use the left-side menu to navigate to the
articletable, then select Relationships, as shown in the following illustration, then click Add and Save.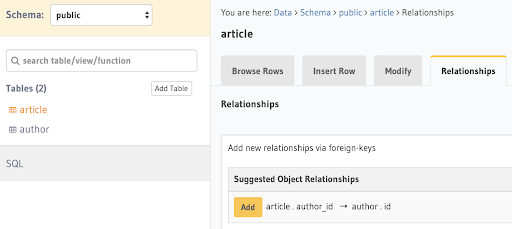
-
To create an array relationship, use the left-side menu to navigate to the
authortable, then select Relationships, as shown in the following illustration, then click Add and Save.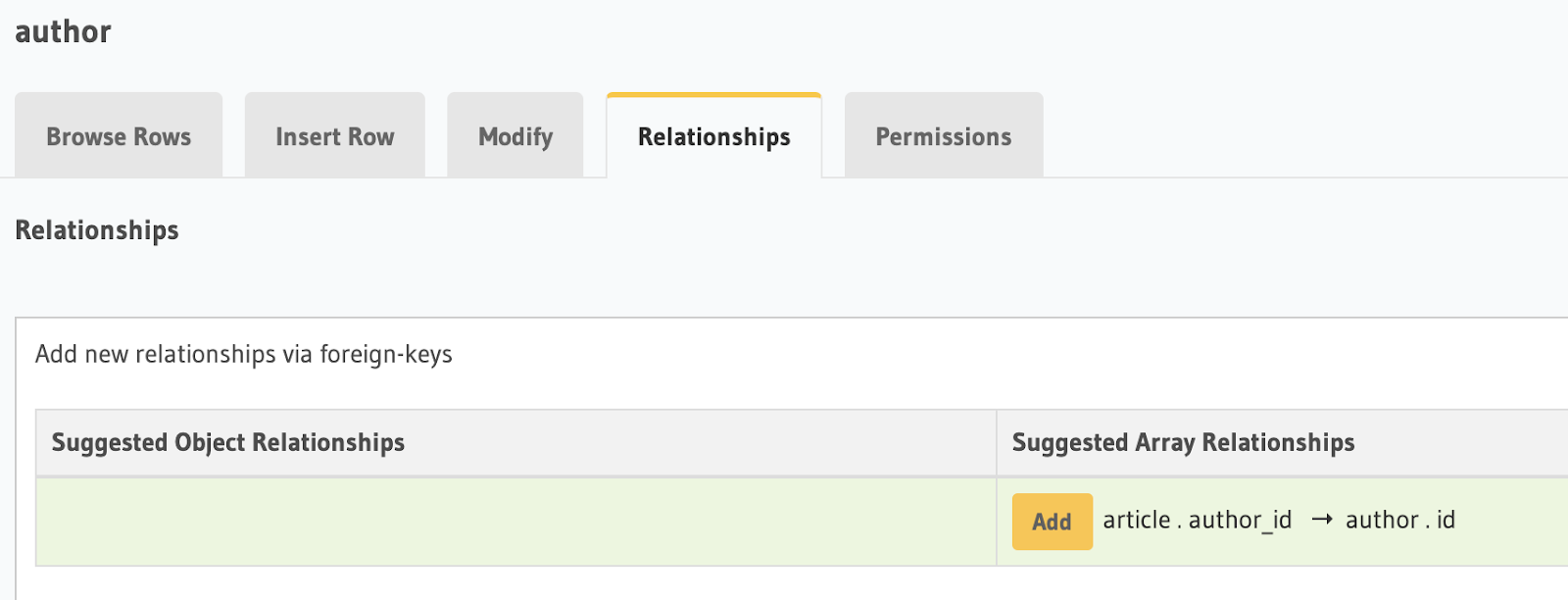
Finally, load sample data, as follows:
-
On the command line, change your directory to the root
yugabytedirectory, and then open ysqlsh to connect to the YugabyteDB cluster, as follows:$ ./bin/ysqlsh -
Copy and paste the following YSQL statements into the shell and then press Enter:
INSERT INTO author(name) VALUES ('John Doe'), ('Jane Doe'); INSERT INTO article(title, content, rating, author_id) VALUES ('Jane''s First Book', 'Lorem ipsum', 10, 2); INSERT INTO article(title, content, rating, author_id) VALUES ('John''s First Book', 'dolor sit amet', 8, 1); INSERT INTO article(title, content, rating, author_id) VALUES ('Jane''s Second Book', 'consectetur adipiscing elit', 7, 2); INSERT INTO article(title, content, rating, author_id) VALUES ('Jane''s Third Book', 'sed do eiusmod tempor', 8, 2); INSERT INTO article(title, content, rating, author_id) VALUES ('John''s Second Book', 'incididunt ut labore', 9, 1); SELECT * FROM author ORDER BY id; SELECT * FROM article ORDER BY id;
Running GraphQL queries
To run GraphQL queries, return to Hasura and click GRAPHIQL.
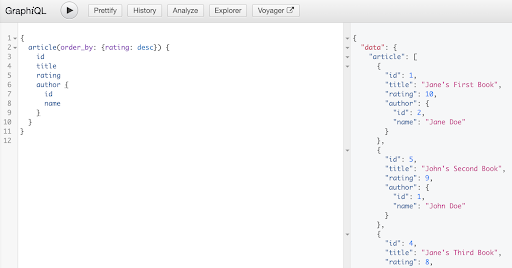
You can query the database using the object relationship. The following example shows how to obtain a list of articles and sort each article’s author in descending order and by rating:
{
article(order_by: {rating: desc}) {
id
title
author {
id
name
}
}
}
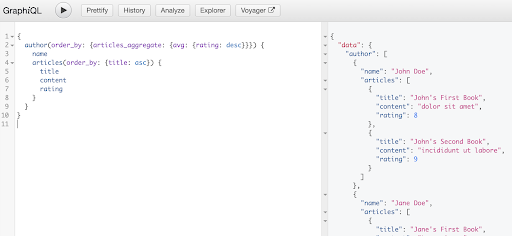
You can also query the database using the array relationship. The following example shows how to obtain a list of authors and a nested list of each author’s articles where the authors are ordered by descending by the average ratings of their articles, and their article lists are ordered by title:
{
author(order_by: {articles_aggregate: {avg: {rating: desc}}}) {
name
articles(order_by: {title: asc}) {
title
content
rating
}
}
}
Clean-up
Optionally, you can stop YugabyteDB and Hasura, as follows:
-
Stop the YugabyteDB cluster by executing the following command:
./bin/yugabyted stop -
Stop the Hasura container by executing the following command:
docker stop <container-id>
To list running containers, execute the following command:
docker ps