Prometheus integration
You can monitor your local YugabyteDB cluster with a local instance of Prometheus, a popular standard for time series monitoring of cloud native infrastructure. YugabyteDB services and APIs expose metrics in the Prometheus format at the /prometheus-metrics endpoint. For details on the metrics targets for YugabyteDB, see Prometheus monitoring.
Setup
Download and install Prometheus
Download Prometheus and refer to Get Started with Prometheus for installation instructions.
Create a universe
Set up a local cluster
If a local universe is currently running, first destroy it.
Start a local three-node universe with an RF of 3 by first creating a single node, as follows:
./bin/yugabyted start \
--advertise_address=127.0.0.1 \
--base_dir=${HOME}/var/node1 \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-2.us-east-2a
On macOS, the additional nodes need loopback addresses configured, as follows:
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.2
sudo ifconfig lo0 alias 127.0.0.3
Next, join more nodes with the previous node as needed. yugabyted automatically applies a replication factor of 3 when a third node is added.
Start the second node as follows:
./bin/yugabyted start \
--advertise_address=127.0.0.2 \
--base_dir=${HOME}/var/node2 \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-2.us-east-2b \
--join=127.0.0.1
Start the third node as follows:
./bin/yugabyted start \
--advertise_address=127.0.0.3 \
--base_dir=${HOME}/var/node3 \
--cloud_location=aws.us-east-2.us-east-2c \
--join=127.0.0.1
After starting the yugabyted processes on all the nodes, configure the data placement constraint of the universe, as follows:
./bin/yugabyted configure data_placement --base_dir=${HOME}/var/node1 --fault_tolerance=zone
This command can be executed on any node where you already started YugabyteDB.
To check the status of a running multi-node universe, run the following command:
./bin/yugabyted status --base_dir=${HOME}/var/node1
Run the YugabyteDB workload generator
Download the YugabyteDB workload generator JAR file (yb-sample-apps.jar) using the following command:
wget https://github.com/yugabyte/yb-sample-apps/releases/download/v1.4.1/yb-sample-apps.jar -O yb-sample-apps.jar
Run the CassandraKeyValue workload application in a separate shell.
java -jar ./yb-sample-apps.jar \
--workload CassandraKeyValue \
--nodes 127.0.0.1:9042 \
--num_threads_read 1 \
--num_threads_write 1
Prepare Prometheus configuration file
From your Prometheus home directory, create a file yugabytedb.yml and add the following:
global:
scrape_interval: 5s # Set the scrape interval to every 5 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 5s # Evaluate rules every 5 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# YugabyteDB configuration to scrape Prometheus time series metrics
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "yugabytedb"
metrics_path: /prometheus-metrics
relabel_configs:
- target_label: "node_prefix"
replacement: "cluster-1"
metric_relabel_configs:
# Save the name of the metric so we can group_by since we cannot by __name__ directly...
- source_labels: ["__name__"]
regex: "(.*)"
target_label: "saved_name"
replacement: "$1"
# The following basically retrofit the handler_latency_* metrics to label format.
- source_labels: ["__name__"]
regex: "handler_latency_(yb_[^_]*)_([^_]*)_([^_]*)(.*)"
target_label: "server_type"
replacement: "$1"
- source_labels: ["__name__"]
regex: "handler_latency_(yb_[^_]*)_([^_]*)_([^_]*)(.*)"
target_label: "service_type"
replacement: "$2"
- source_labels: ["__name__"]
regex: "handler_latency_(yb_[^_]*)_([^_]*)_([^_]*)(_sum|_count)?"
target_label: "service_method"
replacement: "$3"
- source_labels: ["__name__"]
regex: "handler_latency_(yb_[^_]*)_([^_]*)_([^_]*)(_sum|_count)?"
target_label: "__name__"
replacement: "rpc_latency$4"
static_configs:
- targets: ["127.0.0.1:7000", "127.0.0.2:7000", "127.0.0.3:7000"]
labels:
export_type: "master_export"
- targets: ["127.0.0.1:9000", "127.0.0.2:9000", "127.0.0.3:9000"]
labels:
export_type: "tserver_export"
- targets: ["127.0.0.1:12000", "127.0.0.2:12000", "127.0.0.3:12000"]
labels:
export_type: "cql_export"
- targets: ["127.0.0.1:13000", "127.0.0.2:13000", "127.0.0.3:13000"]
labels:
export_type: "ysql_export"
- targets: ["127.0.0.1:11000", "127.0.0.2:11000", "127.0.0.3:11000"]
labels:
export_type: "redis_export"
Start Prometheus server
Start the Prometheus server from the Prometheus home directory as follows:
./prometheus --config.file=yugabytedb.yml
Open the Prometheus UI at http://localhost:9090 and then navigate to the Targets page under Status.
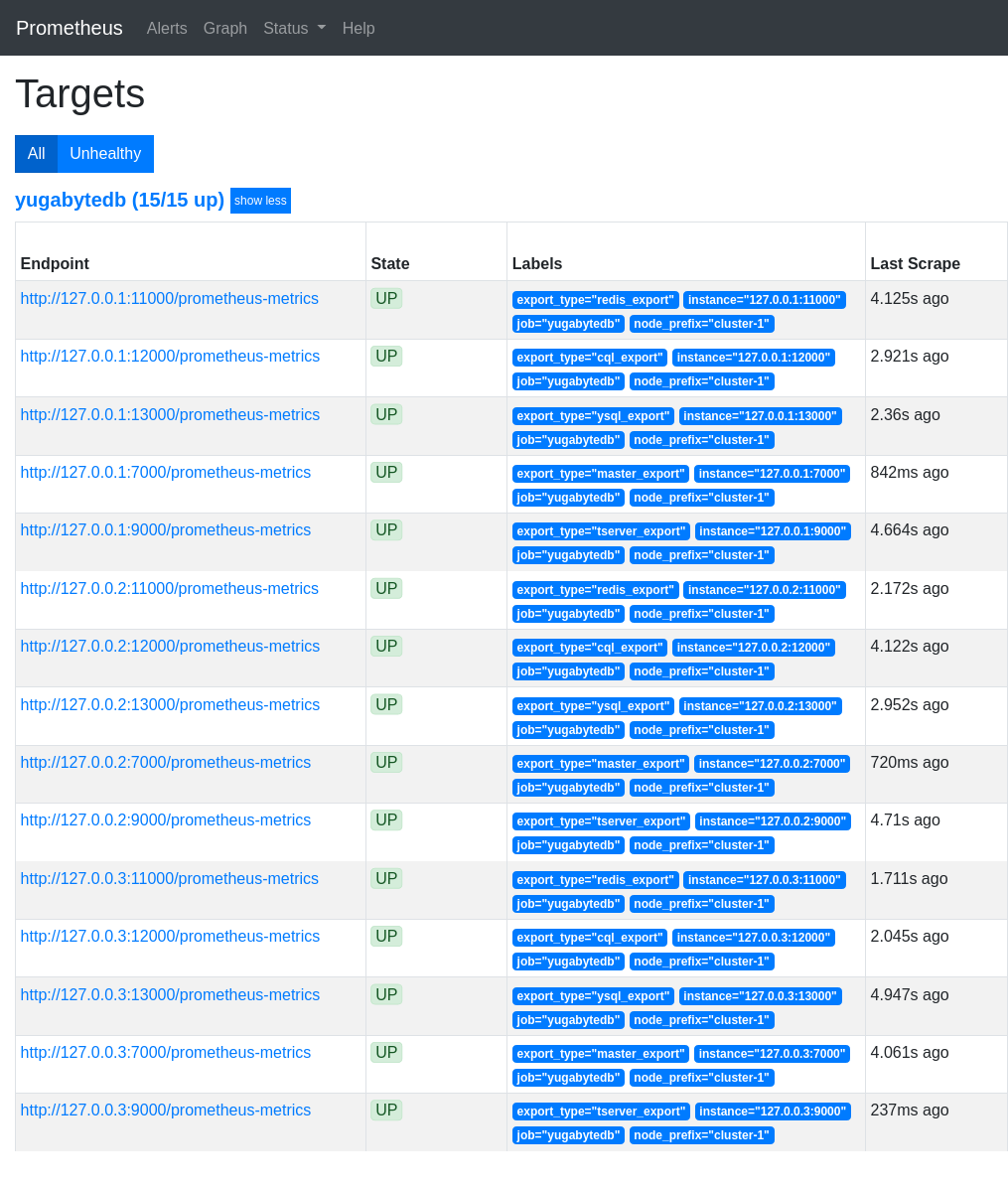
Analyze key metrics
On the Prometheus Graph UI, you can plot the read or write throughput and latency for the CassandraKeyValue sample application. Because the source code of the application uses only SELECT statements for reads and INSERT statements for writes (aside from the initial CREATE TABLE), you can measure throughput and latency by using the metrics corresponding to the SELECT and INSERT statements.
Paste the following expressions into the Expression box and click Execute followed by Add Graph.
Throughput
Read IOPS
sum(irate(rpc_latency_count{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="SelectStmt"}[1m]))
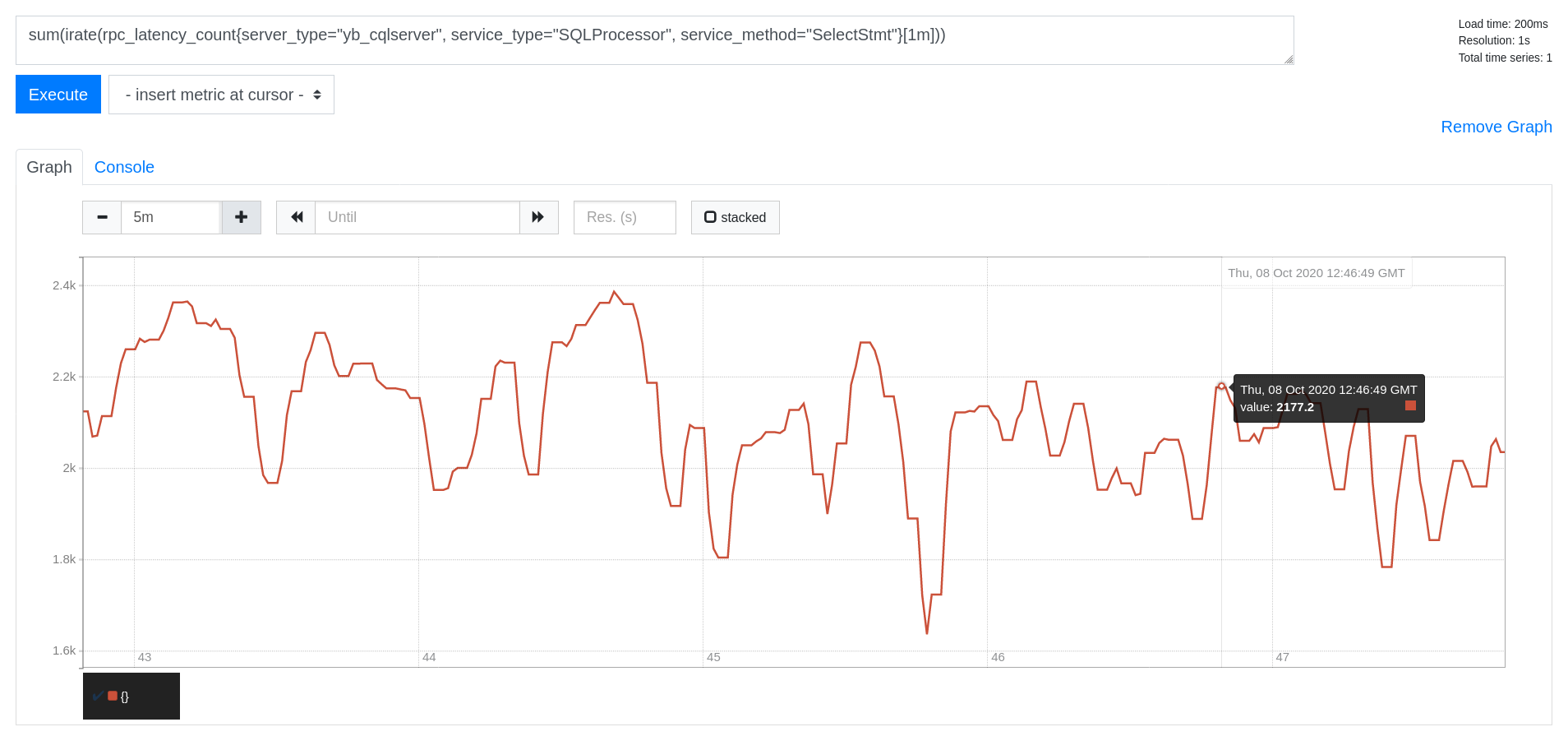
Write IOPS
sum(irate(rpc_latency_count{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="InsertStmt"}[1m]))
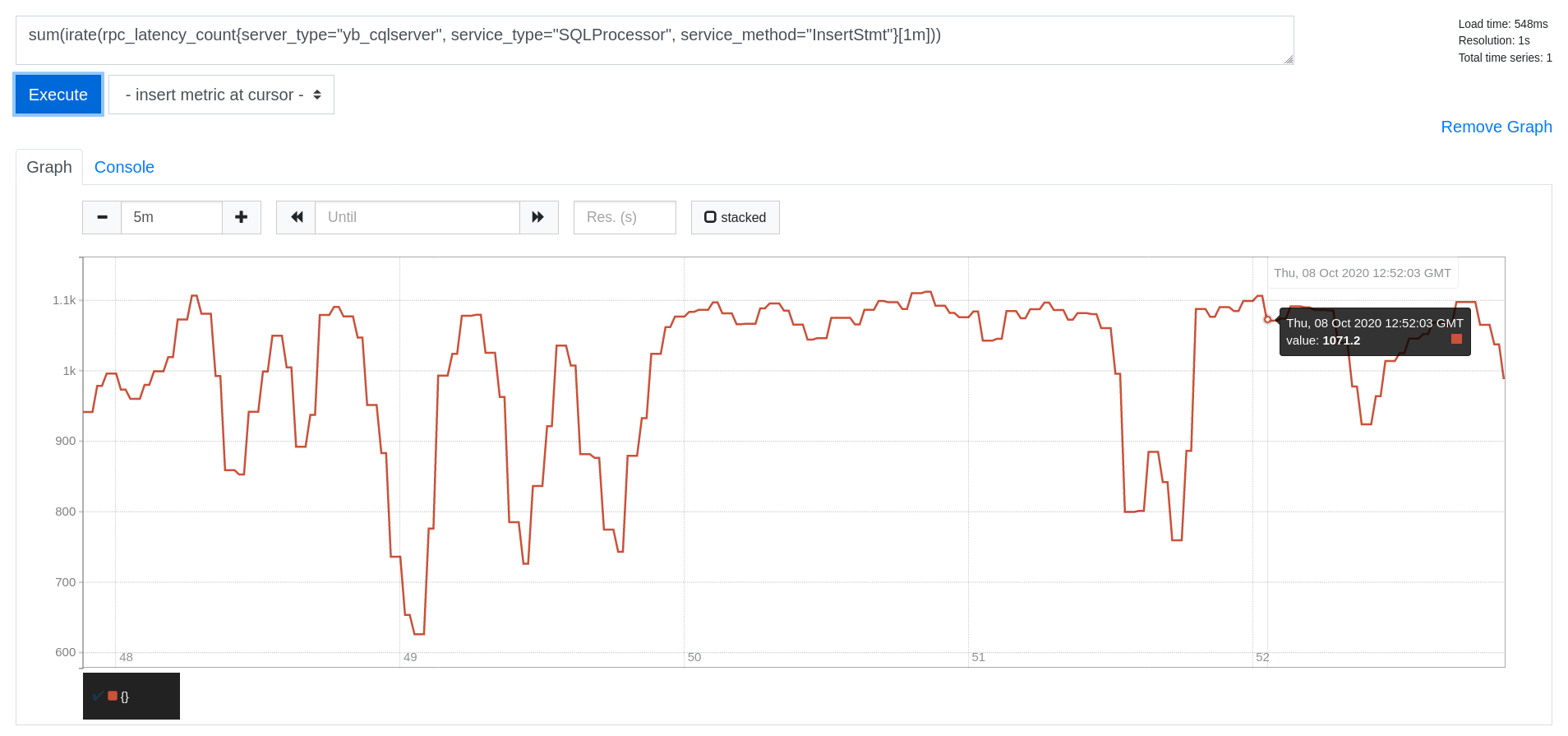
Latency
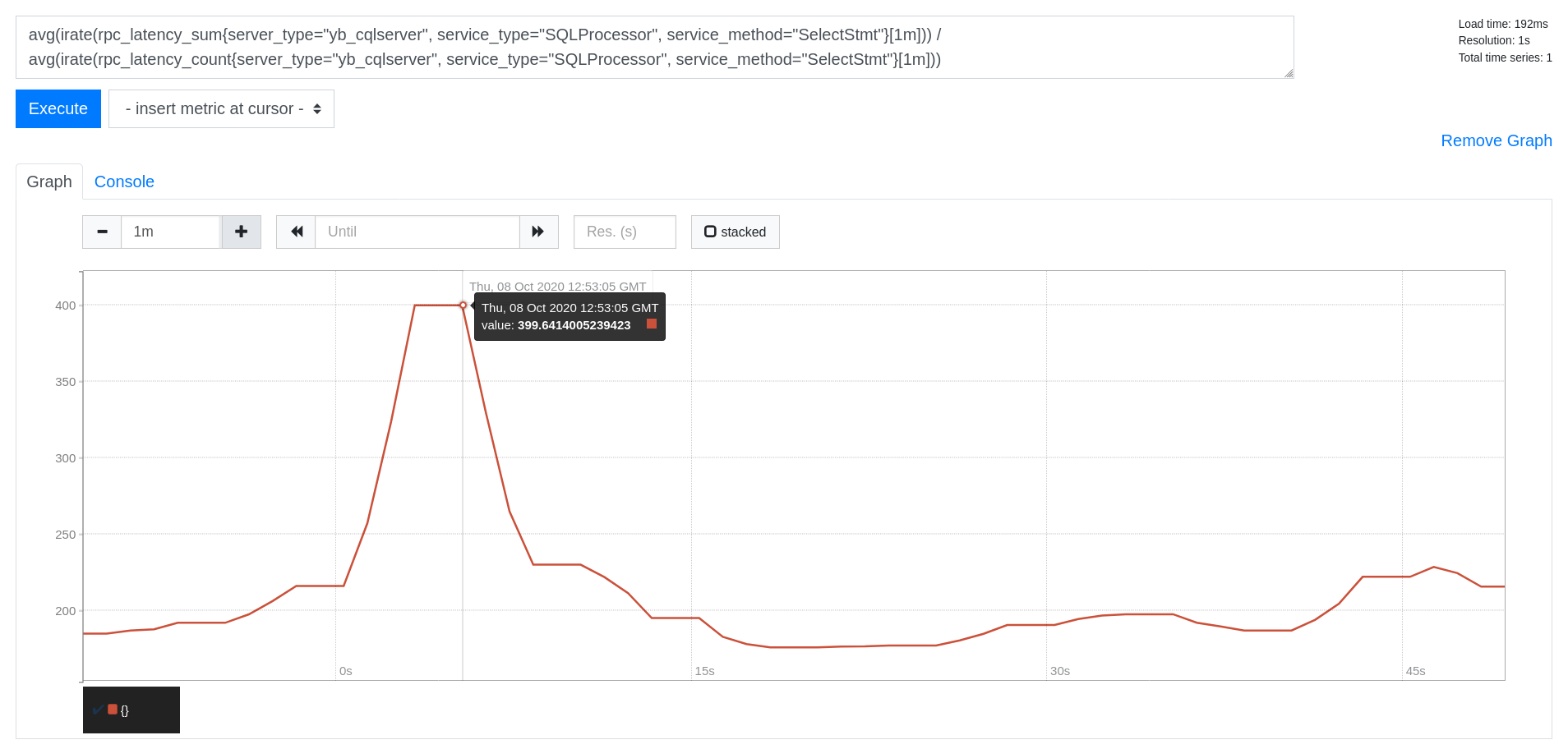
Read Latency (in microseconds)
avg(irate(rpc_latency_sum{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="SelectStmt"}[1m])) /
avg(irate(rpc_latency_count{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="SelectStmt"}[1m]))
Write Latency (in microseconds)
avg(irate(rpc_latency_sum{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="InsertStmt"}[1m])) /
avg(irate(rpc_latency_count{server_type="yb_cqlserver", service_type="SQLProcessor", service_method="InsertStmt"}[1m]))
What's next?
Set up Grafana dashboards for better visualization of the metrics being collected by Prometheus.