YugabyteDB gRPC Connector
The YugabyteDB gRPC Connector is based on the Debezium Connector, and captures row-level changes in a YugabyteDB database's schemas using the YugabyteDB gRPC replication protocol.
Connector compatibility
The connector is compatible with the following versions of YugabyteDB.
| YugabyteDB | Connector |
|---|---|
| 2.14 | 1.9.5.y.3 |
| 2.16 | 1.9.5.y.24 |
| 2.18.2 | 1.9.5.y.33.2 |
| 2.20 | 1.9.5.y.220.2 |
In addition, the connector supports the following:
- Kafka Connect v2.x and later.
- YugabyteDB v2.14 and later.
Note
Starting with YugabyteDB v2.20, the naming convention for releases of the connector uses the scheme major.y.minor, as follows:
- major - Debezium release the connector is based on
- minor - version of YugabyteDB the connector works with
The connector is backward compatible with previous releases of YugabyteDB unless stated otherwise.
Initial Snapshot and Continuous Streaming
- Initial Snapshot: Upon its first connection to a YugabyteDB cluster, the connector takes a consistent snapshot of the configured tables.
- Continuous Streaming: After the snapshot, it continuously captures row-level changes (insertions, updates, and deletions) from the database. It then generates data change event records and streams them to Kafka topics.
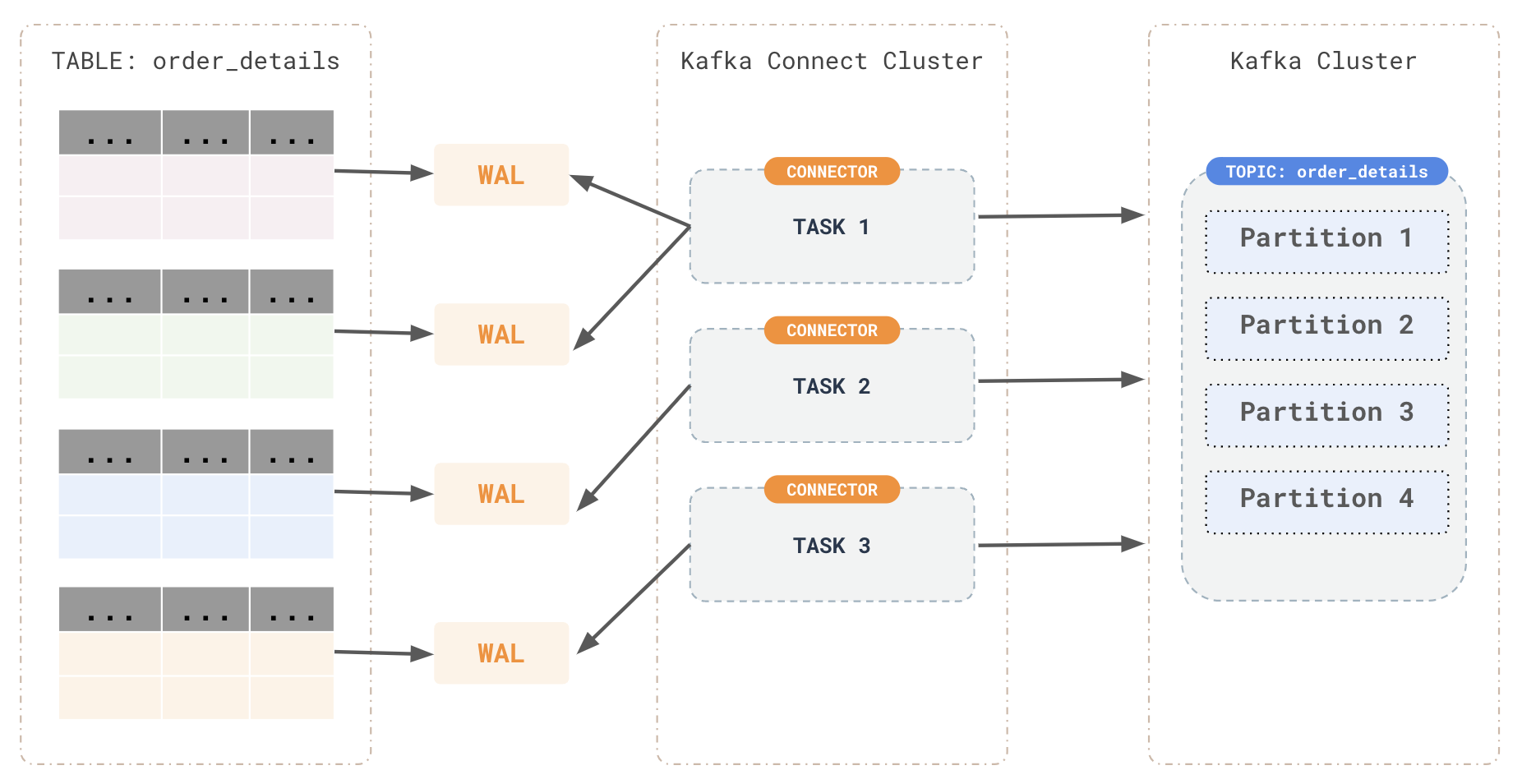
Kafka integration
For each table, the connector streams all generated events to a separate Kafka topic. Client applications and services can consume these data change event records from their respective topics.
- CDC (Change Data Capture) Service: The Debezium connector leverages the CDC service APIs to read the changes from YugabyteDB.
- Event Production: For every row-level insert, update, and delete operation captured, the connector produces a corresponding change event and sends it to separate Kafka topics dedicated to each table.
- Client Consumption: Applications read the Kafka topics corresponding to the database tables they are interested in and react to the row-level events received.
Failure tolerance
The connector records the WAL position for each event as it reads changes and produces events. If the connector stops (due to communication failures, network problems, or crashes), it resumes reading the WAL from the last recorded position upon restart. This uses checkpoints managed on both the Kafka side and the YugabyteDB cluster.
How the connector works
To optimally configure and run a Debezium connector, it is helpful to understand how the connector performs snapshots, streams change events, determines Kafka topic names, and uses metadata.
Security
Currently, for any user that has the access to the cluster, authentication is done via that user. SSL support-based verification is provided for all the required keys and certificates are passed to the connector.
Note
Per-user CDC privileges are planned for a future release.Snapshots
Most YugabyteDB servers are configured to not retain the complete history of the database in the WAL segments. This means that the YugayteDB connector would be unable to see the entire history of the database by reading only the WAL. Consequently, the first time that the connector starts, it performs an initial consistent snapshot of the database. You can change this behavior by setting the snapshot.mode connector configuration property to a value other than initial.
After the connector completes its initial snapshot, it continues streaming the changes. This ensures that the connector does not miss any updates. If the connector stops again for any reason, upon restart, the connector continues streaming changes from where it previously left off.
Options for the snapshot.mode connector configuration property are as follows:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
never |
The connector never performs a snapshot. When a connector is configured in this way, the behaviour is as follows. If an offset is stored on the server, the connector will resume the streaming from that position. If no offset is stored on the server, the connector will bootstrap the tablets, meaning that it will stream data from that point onwards only, and then start streaming. The never snapshot mode is useful when you know that your data of interest will be coming after the point you have deployed your connector. |
initial |
The connector performs a snapshot every time it starts. When a connector is configured this way, the behaviour is as follows. If the snapshot was stopped midway, the connector continues to take the snapshot from that position. If the snapshot was completed previously for the given stream ID, then the connector resumes streaming from the point checkpoints are stored on the server. |
initial_only |
The connector performs a database snapshot and stops before streaming any change event records. If the connector had started but did not complete a snapshot before stopping, the connector resumes the snapshot process from the point it stopped and stops when the snapshot completes. |
Streaming changes
The YugabyteDB gRPC Connector typically spends the vast majority of its time streaming changes from the YugabyteDB server to which it is connected.
The connector keeps polling for changes and whenever there is a change, the connector processes them, converts them to a specific format (Protobuf or JSON in the case of the Debezium plugin) and writes them on an output stream, which can then be consumed by clients.
The connector acts as a YugabyteDB client. When the connector receives changes it transforms the events into Debezium create, update, or delete events that include the LSN of the event. The connector forwards these change events in records to the Kafka Connect framework, which is running in the same process. The Kafka Connect process asynchronously writes the change event records in the same order in which they were generated to the appropriate Kafka topic.
Periodically, Kafka Connect records the most recent offset in another Kafka topic. The offset indicates source-specific position information that Debezium includes with each event.
When Kafka Connect gracefully shuts down, it stops the connectors, and flushes all event records to Kafka. Upon restart, the connector reads the last recorded offset from YugabyteDB server and then it sends a request to the YugabyteDB server to send the events starting just after that position.
Schema changes
The connector retrieves schema information as part of the change events which consist of the schema metadata for the table. When there is any schema change on the configured table, the connector will automatically receive an event pertaining to the change and it will update its internal schema.Topic names
By default, the YugabyteDB gRPC connector writes change events for all INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations that occur in a table to a single Apache Kafka topic that is specific to that table. The connector names change event topics as serverName.schemaName.tableName.
The components of a topic name are as follows:
- serverName - the logical name of the connector, as specified by the
database.server.nameconfiguration property. - schemaName - the name of the database schema in which the change event occurred.
- tableName - the name of the database table in which the change event occurred.
For example, suppose that dbserver is the logical server name in the configuration for a connector that is capturing changes in a YugabyteDB installation that has a yugabyte database and an inventory schema that contains four tables: products, products_on_hand, customers, and orders. The connector would stream records to these four Kafka topics:
dbserver.inventory.productsdbserver.inventory.products_on_handdbserver.inventory.customersdbserver.inventory.orders
Now suppose that the tables are not part of a specific schema but were created in the default public YugabyteDB schema. The names of the Kafka topics would be:
dbserver.public.productsdbserver.public.products_on_handdbserver.public.customersdbserver.public.orders
The connector applies similar naming conventions to label its transaction metadata topics.
If the default topic names don't meet your requirements, you can configure custom topic names. To configure custom topic names, you specify regular expressions in the logical topic routing SMT. For more information about using the logical topic routing SMT to customize topic naming, see the Debezium documentation on Topic routing.
Meta information
In addition to the data change event, each record produced by the connector contains some metadata. Metadata includes information about which tablet caused the change event to occur, the commit time, table, database, offset of the event, for example:
"source": {
"version": "1.9.5.y.21",
"connector": "yugabytedb",
"name": "dbserver1",
"snapshot": "false",
"db": "yugabyte",
"sequence": "[null,\"1:4::0:0\"]",
"schema": "public",
"table": "customers",
"txId": "",
"lsn": "1:4::0:0"
}
versionis the version number of the connector which is being used.namealways defaults to thedatabase.server.nameconnector configuration property.dbis the database name on which the connector is configured.sequenceandlsnindicate the offset to which the change event belongs.schemais the schema name to which the table belongs.tableis the name of the table to which the change event belongs.txIdcontains the transaction ID if the change event is a part of any transaction; otherwise it is empty.
Transaction metadata
Debezium can generate events that represent transaction boundaries and that enrich data change event messages.
Note
Debezium registers and receives metadata only for transactions that occur after you deploy the connector. Metadata for transactions that occur before you deploy the connector is not available.For every transaction BEGIN and END, Debezium generates an event containing the following fields:
status-BEGINorENDid- string representation of unique transaction identifierevent_count(forENDevents) - total number of events emitted by the transactiondata_collections(forENDevents) - an array of pairs ofdata_collectionandevent_countthat provides the number of events emitted by changes originating from given data collection
For example:
{
"status": "BEGIN",
"id": "571",
"event_count": null,
"data_collections": null
}
{
"status": "END",
"id": "571",
"event_count": 2,
"data_collections": [
{
"data_collection": "s1.a",
"event_count": 1
},
{
"data_collection": "s2.a",
"event_count": 1
}
]
}
Unless overridden via the transaction.topic option, transaction events are written to the topic and named database.server.name.transaction.
Change data event enrichment
When transaction metadata is enabled the data message Envelope is enriched with a new transaction field. This field provides information about every event in the form of a composite of fields:
id- string representation of unique transaction identifiertotal_order- absolute position of the event among all events generated by the transactiondata_collection_order- the per-data collection position of the event among all events emitted by the transaction
For example:
{
"before": null,
"after": {
"pk": "2",
"aa": "1"
},
"source": {
...
},
"op": "c",
"ts_ms": "1580390884335",
"transaction": {
"id": "571",
"total_order": "1",
"data_collection_order": "1"
}
}
Data change events
The connector generates a data change event for each row-level INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operation. Each event contains a key and a value. The structure of the key and the value depends on the table that was changed.
Debezium and Kafka Connect are designed around continuous streams of event messages. However, the structure of these events may change over time, which can be difficult for consumers to handle. To address this, each event contains the schema for its content. This makes each event self-contained.
The following skeleton JSON shows the basic four parts of a change event. However, how you configure the Kafka Connect converter that you choose to use in your application determines the representation of these four parts in change events. A schema field is in a change event only when you configure the converter to produce it. Likewise, the event key and event payload are in a change event only if you configure a converter to produce it.
If you use the JSON converter and you configure it to produce all four basic change event parts, change events have the following structure:
{
"schema": { --> 1
...
},
"payload": { --> 2
...
},
"schema": { --> 3
...
},
"payload": { --> 4
...
}
}
| Item | Field name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | schema | The first schema field is part of the event key. It specifies a Kafka Connect schema that describes what is in the event key's payload portion. In other words, the first schema field describes the structure of the primary key, or the unique key if the table does not have a primary key, for the table that was changed. |
| 2 | payload | The first payload field is part of the event key. It has the structure described by the previous schema field and it contains the key for the row that was changed. |
| 3 | schema | The second schema field is part of the event value. It specifies the Kafka Connect schema that describes what is in the event value's payload portion. In other words, the second schema describes the structure of the row that was changed. Typically, this schema contains nested schemas. |
| 4 | payload | The second payload field is part of the event value. It has the structure described by the previous schema field and it contains the actual data for the row that was changed. |
Naming conflicts due to invalid characters
The YugabyteDB gRPC connector ensures that all Kafka Connect schema names adhere to the Avro schema name format. This means that the logical server name must start with a Latin letter or an underscore (a-z, A-Z, or _). Each remaining character in the logical server name and each character in the schema and table names must be a Latin letter, a digit, or an underscore (a-z, A-Z, 0-9, or _). Invalid characters are replaced with an underscore character.
This can lead to unexpected conflicts if the logical server name, a schema name, or a table name contains invalid characters, in the event that the only characters that distinguish names from one another are invalid, and thus replaced with underscores.
Change event keys
For a given table, the change event's key has a structure that contains a field for each column in the primary key of the table at the time the event was created.
Consider a customers table defined in the public database schema and the example of a change event key for that table:
CREATE TABLE customers (
id SERIAL,
name VARCHAR(255),
email TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
Example change event key
If the database.server.name connector configuration property has the value dbserver1, every change event for the customers table while it has this definition has the same key structure, which in JSON looks like the following:
{
"schema": { --> 1
"type": "struct",
"name": "dbserver1.public.customers.Key", --> 2
"optional": false, --> 3
"fields": [ --> 4
{
"name": "id",
"index": "0",
"schema": {
"type": "INT32",
"optional": "false"
}
}
]
},
"payload": { --> 5
"id": {
"value":"1"
}
},
}
This change event key has the following structure:
| Item | Field name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | schema | The schema portion of the key specifies a Kafka Connect schema that describes what is in the key's payload portion. |
| 2 | dbserver1.public. customers.Key |
Name of the schema that defines the structure of the key's payload. This schema describes the structure of the primary key for the table that was changed. Key schema names have the format connector-name.database-name.table-name.Key. In this example: dbserver1 is the logical name of the server that generated this event. public is the schema which contains the table which was changed. customers is the table which was updated. |
| 3 | optional | Indicates whether the event key must contain a value in its payload field. In this example, a value in the key's payload is required. |
| 4 | fields | Specifies each field that is expected in the payload, including each field's name, index, and schema. |
| 5 | payload | Contains the key for the row for which this change event was generated. In this example, the key, contains a single id field whose value is 1. |
Note
Although thecolumn.exclude.list and column.include.list connector configuration properties allow you to capture only a subset of table columns, all columns in a primary or unique key are always included in the event's key.
Change event values
The value in a change event is a bit more complicated than the key. Like the key, the value has a schema section and a payload section. The schema section contains the schema that describes the Envelope structure of the payload section, including its nested fields. Change events for operations that create, update or delete data all have a value payload with an envelope structure.
Create events
For a given table, the change event has a structure that contains a field for each column of the table at the time the event was created.
Now suppose a row is inserted to the table:
INSERT INTO customers (name, email) VALUES ('Vaibhav Kushwaha', 'vaibhav@example.com');
The following example shows the value portion of a change event that the connector generates for an operation that creates data in the customers table:
Click to expand the JSON event.
{
"schema": { --> 1
"type": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"type": "struct",
"fields": [ --> 2
{
"type": "int32",
"optional": false,
"field": "id"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "name"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "email"
}
],
"optional": true,
"name": "dbserver1.public.customers.Value",
"field": "before"
},
{
"type": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"type": "int32",
"optional": false,
"field": "id"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "name"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "email"
}
],
"optional": true,
"name": "dbserver1.public.customers.Value",
"field": "after"
},
{
"type": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "version"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "connector"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "name"
},
{
"type": "int64",
"optional": false,
"field": "ts_ms"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"name": "io.debezium.data.Enum",
"version": 1,
"parameters": {
"allowed": "true,last,false"
},
"default": "false",
"field": "snapshot"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "db"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "sequence"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "schema"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "table"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "txId"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": true,
"field": "lsn"
},
{
"type": "int64",
"optional": true,
"field": "xmin"
}
],
"optional": false,
"name": "io.debezium.connector.postgresql.Source",
"field": "source"
},
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "op"
},
{
"type": "int64",
"optional": true,
"field": "ts_ms"
},
{
"type": "struct",
"fields": [
{
"type": "string",
"optional": false,
"field": "id"
},
{
"type": "int64",
"optional": false,
"field": "total_order"
},
{
"type": "int64",
"optional": false,
"field": "data_collection_order"
}
],
"optional": true,
"field": "transaction"
}
],
"optional": false,
"name": "dbserver1.public.customers.Envelope"
},
"payload": { --> 3
"before": null, --> 4
"after": { --> 5
"id": {
"value":1
},
"name": {
"value":"Vaibhav Kushwaha"
},
"email": {
"value":"vaibhav@example.com"
}
},
"source": { --> 6
"version": "1.9.5.y.11",
"connector": "yugabytedb",
"name": "dbserver1",
"ts_ms": -8898156066356,
"snapshot": "false",
"db": "yugabyte",
"sequence": "[null,\"1:4::0:0\"]",
"schema": "public",
"table": "customers",
"txId": "",
"lsn": "1:4::0:0",
"xmin": null
},
"op": "c", --> 7
"ts_ms": 1646145062480, --> 8
"transaction": null
}
}
The fields in the create event are as follows:
| Item | Field name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | schema | Specifies a Kafka Connect schema that describes what is in the event's payload portion. |
| 2 | fields | Fields specified in the schema of the table. |
| 3 | payload | The key for the row for which this change event was generated. |
| 4 | before | Optional field specifying the state of the row before the event occurred. This field is null when the op field is c for create, as in this example, because the change event is for new content. |
| 5 | after | Optional field specifying the state of the row after the event occurred. In this example, the field contains the values of the new row's id, name, and email columns. |
| 6 | source | Mandatory field describing the source metadata for the event. This field contains information you can use to compare this event with other events, with regard to the origin of the events, the order in which the events occurred, and whether the events were part of the same transaction. The source metadata includes:
|
| 7 | op | Mandatory string that describes the type of operation that caused the connector to generate the event. In this example, c indicates that the operation created a row. Valid values are:
|
| 8 | ts_ms | Optional field containing the time at which the connector processed the event. The time is based on the system clock in the JVM running the Kafka Connect task. In the source object, ts_ms indicates the time that the change was made in the database. By comparing the value for payload.source.ts_ms with the value for payload.ts_ms, you can determine the lag between the source database update and Debezium. |
Update events
The value of a change event for an update in the sample customers table has the same schema as a create event for that table. Likewise, the event value's payload has the same structure. However, the event value payload contains different values in an update event.
Note that updating the columns for a row's primary/unique key changes the value of the row's key. When a key changes, Debezium outputs three events: a DELETE event and a tombstone event with the old key for the row, followed by an event with the new key for the row. See Primary key updates on this page for details.
The following example shows a change event value in an event that the connector generates for an update in the customers table:
UPDATE customers SET email = 'service@example.com' WHERE id = 1;
The update event is as follows:
{
"schema": {...},
"payload": {
"before": null, --> 1
"after": { --> 2
"id": {
"value": 1
},
"name": {
"value": "Vaibhav Kushwaha"
},
"email": {
"value": "service@example.com"
}
},
"source": { --> 3
"version": "1.9.5.y.11",
"connector": "yugabytedb",
"name": "dbserver1",
"ts_ms": -8881476960074,
"snapshot": "false",
"db": "yugabyte",
"sequence": "[null,\"1:5::0:0\"]",
"schema": "public",
"table": "customers",
"txId": "",
"lsn": "1:5::0:0",
"xmin": null
},
"op": "u", --> 4
"ts_ms": 1646149134341,
"transaction": null
}
}
The fields in the update event are:
| Item | Field name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | before | The value of the row before the update operation. |
| 2 | after | Specifies the state of the row after the change event happened. In this example, the value of email has now changed to service@example.com. |
| 3 | source | Mandatory field that describes the source metadata for the event. The source field structure has the same fields as a create event, but some values are different. The source metadata includes:
|
| 4 | op | In an update event, this field's value is u, signifying that this row changed because of an update. |
Primary key updates
An UPDATE operation that changes a row's primary key field(s) is known as a primary key change. For a primary key change, in place of sending an UPDATE event record, the connector sends a DELETE event record for the old key, and a CREATE event record for the new (updated) key. These events have the usual structure and content, and in addition, each one has a message header related to the primary key change:
-
The DELETE event record has
__debezium.newkeyas a message header. The value of this header is the new primary key for the updated row. -
The CREATE event record has
__debezium.oldkeyas a message header. The value of this header is the previous (old) primary key for the updated row.
Delete events
The value in a delete change event has the same schema portion as create and update events for the same table. The payload portion in a delete event for the sample customers table looks like the following:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE id = 1;
{
"schema": {...},
"payload": {
"before": { --> 1
"id": {
"value": 1
},
"name": null,
"email": null
},
"after": null, --> 2
"source": {
"version": "1.9.5.y.11",
"connector": "yugabytedb",
"name": "dbserver1",
"ts_ms": -8876894517738,
"snapshot": "false",
"db": "yugabyte",
"sequence": "[null,\"1:6::0:0\"]",
"schema": "public",
"table": "customers",
"txId": "",
"lsn": "1:6::0:0",
"xmin": null
},
"op": "d", --> 3
"ts_ms": 1646150253203,
"transaction": null
}
}
The fields in this event are:
| Item | Field name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | before | The value of the row before the delete event occurred. |
| 2 | after | Optional field specifying the state of the row after the event occurred. In a delete event, this field is null, indicating that the row no longer exists. |
| 3 | op | The field value is d, indicating that the row was deleted. |
A delete change event record provides a consumer with the information it needs to process the removal of this row.
Tombstone events
When a row is deleted, the delete event value still works with log compaction, because Kafka can remove all earlier messages that have that same key. However, for Kafka to remove all messages that have that same key, the message value must be null. To make this possible, the connector follows a delete event with a special tombstone event that has the same key but a null value.
You can configure whether a connector emits tombstone events using its tombstones.on.delete property.
Whether you enable the connector to emit tombstones depends on how topics are consumed in your environment, and on the characteristics of the sink consumer. If your sink consumers rely on tombstone records to indicate when to delete records in downstream data stores, you should configure the connector to emit them.
By default, a connector's tombstones.on.delete property is set to true so that the connector generates a tombstone after each delete event.
If you set the property to false to prevent the connector from saving tombstone records to Kafka topics, the absence of tombstone records might lead to unintended consequences if your sink is not designed to handle it properly. For example, Kafka relies on tombstones during log compaction to remove records related to deleted keys.
Datatype mappings
The connector represents changes to rows with events that are structured like the table in which the row exists. The event contains a field for each column value. How that value is represented in the event depends on the YugabyteDB data type of the column. The following sections describe how the connector maps YugabyteDB data types to a literal type and a semantic type in event fields.
- The literal type describes how the value is literally represented using Kafka Connect schema types: INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, FLOAT32, FLOAT64, BOOLEAN, STRING, BYTES, ARRAY, MAP, and STRUCT.
- The semantic type describes how the Kafka Connect schema captures the meaning of the field using the name of the Kafka Connect schema for the field.
Default values
If there is a default value for any column in a the YugabyteDB database schema, the connector propagates the same value to the Kafka schema.
Basic types
The following table describes mappings for YugabyteDB basic data types.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| BOOLEAN | BOOLEAN | N/A |
| BIT(1) | STRING | N/A |
| BIT( > 1) | STRING | N/A |
| VARBIT[(M)] | STRING | N/A |
| SMALLINT, SMALLSERIAL | INT16 | N/A |
| INTEGER, SERIAL | INT32 | N/A |
| BIGINT, BIGSERIAL | INT64 | N/A |
| REAL | FLOAT32 | N/A |
| DOUBLE PRECISION | FLOAT64 | N/A |
| CHAR [(M)] | STRING | N/A |
| VARCHAR [(M)] | STRING | N/A |
| TEXT | STRING | N/A |
| TIMESTAMPTZ | STRING | io.debezium.time.ZonedTimestamp A string representation of a timestamp with timezone information, where the timezone is GMT. |
| TIMETZ | STRING | io.debezium.time.ZonedTime A string representation of a time value with timezone information, where the timezone is GMT. |
| INTERVAL [P] | INT64 | io.debezium.time.MicroDuration (default) The approximate number of microseconds for a time interval using the 365.25 / 12.0 formula for days per month average. |
| INTERVAL [P] | STRING | io.debezium.time.Interval (when interval.handling.mode is string) The string representation of the interval value that follows the pattern P<years>Y<months>M<days>DT<hours>H<minutes>M<seconds>S. For example, P1Y2M3DT4H5M6.78S. |
| BYTEA | STRING | A hex encoded string. |
| JSON, JSONB | STRING | io.debezium.data.Json Contains the string representation of a JSON document, array, or scalar. |
| UUID | STRING | io.debezium.data.Uuid Contains the string representation of a YugabyteDB UUID value. |
| DATE | INT32 | Number of days since the UNIX epoch (January 1, 1970). |
| TIME | INT32 | Milliseconds since midnight. |
| TIMESTAMP | INT64 | Milliseconds since the UNIX epoch (1970-01-01 00:00:00). |
| INT4RANGE | STRING | Range of integer. |
| INT8RANGE | STRING | Range of bigint. |
| NUMRANGE | STRING | Range of numeric. |
| TSRANGE | STRING | The string representation of a timestamp range without a time zone. |
| TSTZRANGE | STRING | The string representation of a timestamp range with the local system time zone. |
| DATERANGE | STRING | The string representation of a date range. Always has an exclusive upper bound. |
| ARRAY | ARRAY | N/A |
| ENUM | STRING | The string representation of the enum label. |
Temporal types
Other than YugabyteDB's TIMESTAMPTZ and TIMETZ data types, which contain time zone information, how temporal types are mapped depends on the value of the time.precision.mode connector configuration property. The following sections describe these mappings:
time.precision.mode=adaptivetime.precision.mode=adaptive_time_microsecondstime.precision.mode=connect
Adaptive mode
When the time.precision.mode property is set to adaptive (the default), the connector determines the literal type and semantic type based on the column's data type definition. This ensures that events exactly represent the values in the database.
The following table describes mappings when time.precision.mode is adaptive.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | INT32 | io.debezium.time.Date The number of days since the epoch. |
| TIME([P]) | INT32 | io.debezium.time.Time The number of milliseconds past midnight, and does not include timezone information. |
| TIMESTAMP([P]) | INT64 | io.debezium.time.Timestamp The number of milliseconds since the epoch, and does not include timezone information. |
Adaptive (microseconds) mode
When the time.precision.mode configuration property is set to adaptive_time_microseconds, the connector determines the literal type and semantic type for temporal types based on the column's data type definition. This ensures that events exactly represent the values in the database, except all TIME fields are captured as microseconds.
The following table describes mappings when time.precision.mode is adaptive_time_microseconds.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | INT32 | io.debezium.time.Date The number of days since the epoch. |
| TIME([P]) | INT64 | io.debezium.time.MicroTime The time value in microseconds and doesn't include timezone information. YugabyteDB allows precision P to be in the range 0-6 to store up to microsecond precision. |
| TIMESTAMP([P]) | INT64 | io.debezium.time.Timestamp The number of milliseconds since the UNIX epoch, and doesn't include timezone information. |
Connect mode
When the time.precision.mode configuration property is set to connect, the connector uses Kafka Connect logical types. This may be beneficial when consumers can handle only the built-in Kafka Connect logical types and are unable to handle variable-precision time values. However, because YugabyteDB supports microsecond precision, the events generated by a connector with the connect time precision mode results in a loss of precision when the database column has a fractional second precision value that is greater than 3.
The following table describes mappings when time.precision.mode is connect.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | INT32 | org.apache.kafka.connect.data.Date The number of days since the UNIX epoch. |
| TIME([P]) | INT64 | org.apache.kafka.connect.data.Time The number of milliseconds since midnight, and doesn't include timezone information. YugabyteDB allows P to be in the range 0-6 to store up to microsecond precision, though this mode results in a loss of precision when P is greater than 3. |
| TIMESTAMP([P]) | INT64 | org.apache.kafka.connect.data.Timestamp The number of milliseconds since the UNIX epoch, and doesn't include timezone information. YugabyteDB allows P to be in the range 0-6 to store up to microsecond precision, though this mode results in a loss of precision when P is greater than 3. |
TIMESTAMP type
The TIMESTAMP type represents a timestamp without time zone information. Such columns are converted into an equivalent Kafka Connect value based on UTC. For example, the TIMESTAMP value 2022-03-03 16:51:30 is represented by an io.debezium.time.Timestamp with the value 1646326290000 when time.precision.mode is set to any value other than connect.
The timezone of the JVM running Kafka Connect and Debezium does not affect this conversion.
YugabyteDB supports using +/-infinity values in TIMESTAMP columns. These special values are converted to timestamps with value 9223372036825200000 in case of positive infinity or -9223372036832400000 in case of negative infinity.
Decimal types
The setting of the connector configuration property decimal.handling.mode determines how the connector maps decimal types.
Note
YugabyteDB doesn't currently support thedecimal.handling.mode property value precise. If that is set, YugabyteDB automatically defaults to double.
When the decimal.handling.mode property is set to double, the connector represents all DECIMAL, NUMERIC, and MONEY values as Java double values and encodes them as shown in the following table.
The following table describes mappings when decimal.handling.mode is double.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| NUMERIC [(M[,D])] | FLOAT64 | |
| DECIMAL [(M[,D])] | FLOAT64 | |
| MONEY [(M[,D])] | FLOAT64 |
The other possible value for decimal.handling.mode is string. In this case, the connector represents DECIMAL, NUMERIC, and MONEY values as their formatted string representation, and encodes them as shown in the following table.
The following table describes mappings when decimal.handling.mode is string.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| NUMERIC [(M[,D])] | STRING | |
| DECIMAL [(M[,D])] | STRING | |
| MONEY [(M[,D])] | STRING |
Network address types
YugabyteDB has data types that can store IPv4, IPv6, and MAC addresses. You should use these types instead of plain text types to store network addresses, as network address types offer input error checking and specialized operators and functions.
The following table describes mappings for network address types.
| YugabyteDB data type | Literal type (schema type) | Semantic type (schema name) |
|---|---|---|
| INET | STRING | IPv4 and IPv6 networks. |
| CIDR | STRING | IPv4 and IPv6 hosts and networks. |
| MACADDR | STRING | MAC addresses. |
| MACADDR8 | STRING | MAC addresses in EUI-64 format. |
Example data type behaviors
| Datatype | What you insert in YSQL | What you get in the Kafka topic | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIGINT | 123456 | 123456 | |
| BIGSERIAL | Cannot insert explicitly | ||
| BIT [ (N) ] | '11011' | "11011" | |
| BIT VARYING [ (n) ] | '11011' | "11011" | |
| BOOLEAN | FALSE | false | |
| BYTEA | E'\001' | "\x01" | |
| CHARACTER [ (N) ] | 'five5' | "five5" | |
| CHARACTER VARYING [ (n) ] | 'sampletext' | "sampletext" | |
| CIDR | '10.1.0.0/16' | "10.1.0.0/16" | |
| DATE | '2021-11-25' | 18956 | The value in the Kafka topic is the number of days since the Unix epoch (1970-01-01). |
| DOUBLE PRECISION | 567.89 | 567.89 | |
| INET | '192.166.1.1' | "192.166.1.1" | |
| INTEGER | 1 | 1 | |
| INTERVAL [ fields ] [ (p) ] | '2020-03-10 00:00:00'::timestamp - '2020-02-10 00:00:00'::timestamp | 2505600000000 | The output value coming up is the equivalent of the interval value in microseconds. So here 2505600000000 means 29 days. |
| JSON | '{"first_name":"vaibhav"}' | "{"first_name":"vaibhav"}" | |
| JSONB | '{"first_name":"vaibhav"}' | "{"first_name": "vaibhav"}" | |
| MACADDR | '2C:54:91:88:C9:E3' | "2c:54:91:88:c9:e3" | |
| MACADDR8 | '22:00:5c:03:55:08:01:02' | "22:00:5c:03:55:08:01:02" | |
| MONEY | '$100.5' | 100.5 | |
| NUMERIC | 34.56 | 34.56 | |
| REAL | 123.4567 | 123.4567 | |
| SMALLINT | 12 | 12 | |
| INT4RANGE | '(4, 14)' | "[5,14)" | |
| INT8RANGE | '(4, 150000)' | "[5,150000)" | |
| NUMRANGE | '(10.45, 21.32)' | "(10.45,21.32)" | |
| TSRANGE | '(1970-01-01 00:00:00, 2000-01-01 12:00:00)' | "("1970-01-01 00:00:00","2000-01-01 12:00:00")" | |
| TSTZRANGE | '(2017-07-04 12:30:30 UTC, 2021-07-04 12:30:30+05:30)' | "("2017-07-04 12:30:30+00","2021-07-04 07:00:30+00")" | |
| DATERANGE | '(2019-10-07, 2021-10-07)' | "[2019-10-08,2021-10-07)" | |
| SMALLSERIAL | Cannot insert explicitly | ||
| SERIAL | Cannot insert explicitly | ||
| TEXT | 'text to verify behaviour' | "text to verify behaviour" | |
| TIME [ (P) ] [ WITHOUT TIME ZONE ] | '12:47:32' | 46052000 | The output value is the number of milliseconds since midnight. |
| TIME [ (p) ] WITH TIME ZONE | '12:00:00+05:30' | "06:30:00Z" | The output value is the equivalent of the inserted time in UTC. The Z stands for Zero Timezone. |
| TIMESTAMP [ (p) ] [ WITHOUT TIME ZONE ] | '2021-11-25 12:00:00' | 1637841600000 | The output value is the number of milliseconds since the UNIX epoch (January 1, 1970, at midnight). |
| TIMESTAMP [ (p) ] WITH TIME ZONE | '2021-11-25 12:00:00+05:30' | "2021-11-25T06:30:00Z" | This output value is the timestamp value in UTC wherein the Z stands for Zero Timezone and T acts as a separator between the date and time. This format is defined by the sensible practical standard ISO 8601. |
| UUID | 'ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff' | "ffffffff-ffff-ffff-ffff-ffffffffffff" |
Unsupported data types
Support for the following YugabyteDB data types will be enabled in future releases:
- BOX
- CIRCLE
- LINE
- LSEG
- PATH
- PG_LSN
- POINT
- POLYGON
- TSQUERY
- TSVECTOR
- TXID_SNAPSHOT
Setting up YugabyteDB
Before using the connector to monitor the changes on a YugabyteDB server, you need to ensure the following:
- You have a stream ID created on the database you want to monitor the changes for. The stream can be created using the yb-admin create_change_data_stream command.
- The table which is supposed to be monitored should have a primary key. Only tables which have a primary key can be streamed.
WAL disk space consumption
In certain cases, it is possible for YugabyteDB disk space consumed by WAL files to spike or increase out of proportion. There are some possible reasons for this.
For example, the connector is lagging behind in streaming the changes. In this case, the latest checkpoint the connector has received is way behind the last record available in WAL. Because the latest changes are not consumed yet, CDC will not allow the WAL files to be cleaned up, thus causing higher disk consumption. This is the expected behaviour and no action is needed. However, the efficiency of the connector can be increased by increasing the number of tasks so that more processing can happen in parallel.
Deployment
To deploy a Debezium connector, you install the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector archive, configure the connector, and start the connector by adding its configuration to Kafka Connect. For complete steps, follow the guide to running the Debezium connector in YugabyteDB.
Connector configuration example
Following is an example of the configuration for a connector that connects to a YugabyteDB server on port 5433 at 127.0.0.1, whose logical name is dbserver1. Typically, you configure the connector in a JSON file by setting the configuration properties available for the connector.
You can choose to produce events for a subset of the schemas and tables in a database. Optionally, you can ignore, mask, or truncate columns that contain sensitive data, are larger than a specified size, or that you do not need.
{
"name": "ybconnector", --> 1
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.YugabyteDBConnector", --> 2
"database.hostname": "127.0.0.1", --> 3
"database.port": "5433", --> 4
"database.master.addresses": "127.0.0.1:7100", --> 5
"database.streamid": "d540f5e4890c4d3b812933cbfd703ed3", --> 6
"database.user": "yugabyte", --> 7
"database.password": "yugabyte", --> 8
"database.dbname": "yugabyte", --> 9
"database.server.name": "dbserver1", --> 10
"table.include.list": "public.test" --> 11
}
}
- The name of the connector when registered with a Kafka Connect service.
- The name of this YugabyteDB gRPC Connector class.
- The address of this YugabyteDB server.
- The port number of the YugabyteDB YSQL process.
- List of comma separated values of master nodes of the YugabyteDB server. Usually in the form
host:port. - The DB stream ID created using yb-admin.
- The name of the YugabyteDB user having the privileges to connect to the database.
- The password for the above specified YugabyteDB user.
- The name of the YugabyteDB database to connect to.
- The logical name of the YugabyteDB server/cluster, which forms a namespace and is used in all the names of the Kafka topics to which the connector writes and the Kafka Connect schema names.
- A list of all tables hosted by this server that this connector will monitor. This is optional, and there are other properties for listing the schemas and tables to include or exclude from monitoring.
You can send this configuration with a POST command to a running Kafka Connect service. The service records the configuration and starts one connector task that performs the following actions:
- Connects to the YugabyteDB database.
- Reads the transaction log.
- Streams change event records to Kafka topics.
Custom record extractor
YugabyteDB uses a custom record extractor (YBExtractNewRecordState) so that the sinks understand the format in which data is sent. For example, if you are using a JDBC sink connector, you need to add two more properties to the sink configuration:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
transforms |
unwrap |
transforms.unwrap.type |
io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.transforms.YBExtractNewRecordState |
See Transformers.
Adding connector configuration
To run a connector, create a connector configuration and add the configuration to your Kafka Connect cluster.
Prerequisites
- YugabyteDB is configured for change data capture.
- The YugabyteDB gRPC connector is installed.
Procedure
- Create a configuration for the connector.
- Use the Kafka Connect REST API to add that connector configuration to your Kafka Connect cluster.
Results
After the connector starts, it will perform a snapshot of the tables depending on the configuration and if the connector is set to take snapshots. The connector then starts generating data change events for row-level operations and streaming change event records to Kafka topics.
Connector configuration properties
The connector has many configuration properties that you can use to achieve the right connector behavior for your application. Many properties have default values.
The following properties are required unless a default value is available:
| Property | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| connector.class | N/A | Specifies the connector to use to connect Debezium to the database. For YugabyteDB, use io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.YugabyteDBConnector. |
| database.hostname | N/A | The IP address of the database host machine. For a distributed cluster, use the leader node's IP address. Alternatively, you can specify a comma-separated list of multiple host addresses and corresponding ports (for example,ip1:port1,ip2:port2,ip3:port3). This is useful for connection fail-over. |
| database.port | N/A | The port at which the YSQL process is running. |
| database.master.addresses | N/A | Comma-separated list of host:port values. |
| database.user | N/A | The user which will be used to connect to the database. |
| database.password | N/A | Password for the given user. |
| database.dbname | N/A | The database from which to stream. |
| database.server.name | N/A | Logical name that identifies and provides a namespace for the particular YugabyteDB database server or cluster for which Debezium is capturing changes. This name must be unique, as it's also used to form the Kafka topic. |
| database.streamid | N/A | Stream ID created using yb-admin for Change data capture. |
| table.include.list | N/A | Comma-separated list of table names and schema names, such as public.test or test_schema.test_table_name. |
| table.max.num.tablets | 300 | Maximum number of tablets the connector can poll for. This should be greater than or equal to the number of tablets the table is split into. |
| database.sslmode | disable | Whether to use an encrypted connection to the YugabyteDB cluster. Supported options are:
|
| database.sslrootcert | N/A | The path to the file which contains the root certificate against which the server is to be validated. |
| database.sslcert | N/A | Path to the file containing the client's SSL certificate. |
| database.sslkey | N/A | Path to the file containing the client's private key. |
| schema.include.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match names of schemas for which you want to capture changes. Any schema name not included in schema.include.list is excluded from having its changes captured. By default, all non-system schemas have their changes captured. Do not also set the schema.exclude.list property. |
| schema.exclude.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match names of schemas for which you do not want to capture changes. Any schema whose name is not included in schema.exclude.list has its changes captured, with the exception of system schemas. Do not also set the schema.include.list property. |
| table.include.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for tables whose changes you want to capture. Any table not included in table.include.list does not have its changes captured. Each identifier is of the form schemaName.tableName. By default, the connector captures changes in every non-system table in each schema whose changes are being captured. Do not also set the table.exclude.list property. |
| table.exclude.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match fully-qualified table identifiers for tables whose changes you do not want to capture. Any table not included in table.exclude.list has its changes captured. Each identifier is of the form schemaName.tableName. Do not also set the table.include.list property. |
| column.include.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of columns that should be included in change event record values. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form schemaName.tableName.columnName. Do not also set the column.exclude.list property. |
| column.exclude.list | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of columns that should be excluded from change event record values. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form schemaName.tableName.columnName. Do not also set the column.include.list property. |
| column.truncate.to.length.chars | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of character-based columns. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form schemaName.tableName.columnName. In change event records, values in these columns are truncated if they are longer than the number of characters specified by length in the property name. You can specify multiple properties with different lengths in a single configuration. Length must be a positive integer, for example, column.truncate.to.20.chars. |
| column.mask.with.length.chars | N/A | An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names of character-based columns. Fully-qualified names for columns are of the form schemaName.tableName.columnName. In change event records, the values in the specified table columns are replaced with length number of asterisk (*) characters. You can specify multiple properties with different lengths in a single configuration. Length must be a positive integer or zero. When you specify zero, the connector replaces a value with an empty string. |
| message.key.columns | empty string | A list of expressions that specify the columns that the connector uses to form custom message keys for change event records that it publishes to the Kafka topics for specified tables. By default, Debezium uses the primary key column of a table as the message key for records that it emits. In place of the default, or to specify a key for tables that lack a primary key, you can configure custom message keys based on one or more columns. To establish a custom message key for a table, list the table, followed by the columns to use as the message key. Each list entry takes the following format: <fully-qualified_tableName>:<keyColumn>,<keyColumn>To base a table key on multiple column names, insert commas between the column names. Each fully-qualified table name is a regular expression in the following format: <schemaName>.<tableName> The property can include entries for multiple tables. Use a semicolon to separate table entries in the list. The following example sets the message key for the tables inventory.customers and purchase.orders: inventory.customers:pk1,pk2;purchase.orders:pk3,pk4 For the table inventory.customers, the columns pk1 and pk2 are specified as the message key. For the purchase.orders tables in any schema, the columns pk3 and pk4 server as the message key. There is no limit to the number of columns that you use to create custom message keys. However, it's best to use the minimum number that are required to specify a unique key. |
TLSv1.2 only
The APIs used to fetch the changes are set up to work with TLSv1.2 only. Make sure you're using the proper environment properties for Kafka Connect!Obtaining universe certificates
If you have a YugabyteDB cluster with SSL enabled, you need to obtain the root certificate and provide the path of the file in the database.sslrootcert configuration property. You can follow these links to get the certificates for your universe:
Advanced connector configuration properties:
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| snapshot.mode | N/A | never - Don't take a snapshot initial - Take a snapshot when the connector is first started initial_only - Only take a snapshot of the table, do not stream further changes |
| snapshot.include.collection.list | All tables specified in table.include.list |
An optional, comma-separated list of regular expressions that match the fully-qualified names (<schemaName>.<tableName>) of the tables to include in a snapshot. The specified items must also be named in the connector's table.include.list property. This property takes effect only if the connector's snapshot.mode property is set to a value other than never. |
| cdc.poll.interval.ms | 500 | The interval at which the connector will poll the database for the changes. |
| admin.operation.timeout.ms | 60000 | The default timeout used for administrative operations (such as createTable, deleteTable, getTables, etc). |
| operation.timeout.ms | 60000 | The default timeout used for user operations (using sessions and scanners). |
| socket.read.timeout.ms | 60000 | The default timeout to use when waiting on data from a socket. |
| time.precision.mode | adaptive | Time, date, and timestamps can be represented with different kinds of precision: adaptive captures the time and timestamp values exactly as in the database using millisecond precision values based on the database column's type. adaptive_time_microseconds captures the date, datetime and timestamp values exactly as in the database using millisecond precision values based on the database column's type. An exception is TIME type fields, which are always captured as microseconds. connect always represents time and timestamp values by using Kafka Connect's built-in representations for Time, Date, and Timestamp, which use millisecond precision regardless of the database columns' precision. See temporal values. |
| decimal.handling.mode | double | The precise mode is not currently supported. double maps all the numeric, double, and money types as Java double values (FLOAT64). string represents the numeric, double, and money types as their string-formatted form. |
| binary.handling.mode | hex | hex is the only supported mode. All binary strings are converted to their respective hex format and emitted as their string representation . |
| interval.handling.mode | numeric | Specifies how the connector should handle values for interval columns:numeric represents intervals using approximate number of microseconds. string represents intervals exactly by using the string pattern representationP<years>Y<months>M<days>DT<hours>H<minutes>M<seconds>S.For example: P1Y2M3DT4H5M6.78S. See YugabyteDB data types. |
| transaction.topic | ${database.server.name}.transaction |
Controls the name of the topic to which the connector sends transaction metadata messages. The placeholder ${database.server.name} can be used for referring to the connector's logical name; defaults to ${database.server.name}.transaction, for example dbserver1.transaction. |
| provide.transaction.metadata | false |
Determines whether the connector generates events with transaction boundaries and enriches change event envelopes with transaction metadata. Specify true if you want the connector to do this. See Transaction metadata for details. |
| skipped.operations | N/A | A comma-separated list of operation types to be skipped during streaming. The types are c for insert/create operations, u for update operations, and d for delete operations. By default, no operations are skipped. |
| max.queue.size | 20240 | Positive integer value for the maximum size of the blocking queue. The connector places change events received from streaming replication in the blocking queue before writing them to Kafka. This queue can provide back pressure when, for example, writing records to Kafka is slower that it should be, or when Kafka is not available. |
| max.batch.size | 10240 | Positive integer value that specifies the maximum size of each batch of events that the connector processes. |
| max.queue.size.in.bytes | 0 | Long value for the maximum size in bytes of the blocking queue. The feature is disabled by default, it will be active if it's set with a positive long value. |
| max.connector.retries | 5 | Positive integer value for the maximum number of times a retry can happen at the connector level itself. |
| connector.retry.delay.ms | 60000 | Delay between subsequent retries at the connector level. |
| ignore.exceptions | false |
Determines whether the connector ignores exceptions, which should not cause any critical runtime issues. By default, if there is an exception, the connector throws the exception and stops further execution. Specify true to have the connector log a warning for any exception and proceed. |
| tombstones.on.delete | true |
Controls whether a delete event is followed by a tombstone event.true - a delete operation is represented by a delete event and a subsequent tombstone event.false - only a delete event is emitted.After a source record is deleted, emitting a tombstone event (the default behavior) allows Kafka to completely delete all events that pertain to the key of the deleted row in case log compaction is enabled for the topic. |
| auto.add.new.tables | true |
Controls whether the connector should keep polling the server to check if any new table has been added to the configured change data stream ID. If a new table has been found in the stream ID and if it has been included in the table.include.list, the connector will be restarted automatically. |
| new.table.poll.interval.ms | 300000 | The interval at which the poller thread will poll the server to check if there are any new tables in the configured change data stream ID. |
| transaction.ordering | false |
Whether to order transactions by their commit time. Deprecation Notice This configuration property has been deprecated. For more details, see transaction ordering. |
Transformers
The following three transformers are available: YBExtractNewRecordState, ExtractTopic, and PGCompatible.
YBExtractNewRecordState SMT
Transformer type: io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.transforms.YBExtractNewRecordState
Unlike the Debezium connector for PostgreSQL, the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector only sends the after image of the "set of columns" that are modified. PostgreSQL sends the complete after image of the row which has changed. So by default if the column was not changed, it is not a part of the payload that is sent and the default value is set to null.
To differentiate between the case where a column is set to null and the case in which it's not modified, the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector changes the value type to a struct. In this structure, an unchanged column is {'value': null}, whereas the column changed to a null value is {'value': null, 'set': true}.
A schema registry requires that, once a schema is registered, records must contain only payloads with that schema version. If you're using a schema registry, the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector's approach can be problematic, as the schema may change with every message. For example, if we keep changing the record to only include the value of modified columns, the schema of each record will be different (the total number unique schemas will be a result of making all possible combinations of columns) and thus would require sending a schema with every record.
To avoid this problem when you're using a schema registry, use the YBExtractNewRecordState SMT (Single Message Transformer for Kafka), which interprets these values and sends the record in the correct format (by removing the unmodified columns from the JSON message). Records transformed by YBExtractNewRecordState are compatible with all sink implementations. This approach ensures that the schema doesn't change with each new record and it can work with a schema registry.
ExtractTopic
Transformer type: io.aiven.kafka.connect.transforms.ExtractTopic
This transformer extracts a string value from the record and uses it as the topic name.
The transformation can use either the whole key or value (in this case, it must have INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, FLOAT32, FLOAT32, BOOLEAN, or STRING type) or a field in them (in this case, it must have STRUCT type and the field's value must be INT8, INT16, INT32, INT64, FLOAT32, FLOAT32, BOOLEAN, or STRING).
ExtractTopic exists in two variants:
io.aiven.kafka.connect.transforms.ExtractTopic$Key- works on keysio.aiven.kafka.connect.transforms.ExtractTopic$Value- works on values
The transformation defines the following configurations:
field.name- The name of the field which should be used as the topic name. Ifnullor empty, the entire key or value is used (and assumed to be a string). By default isnull.skip.missing.or.null- In case the source of the new topic name isnullor missing, should a record be silently passed without transformation. By default, isfalse.
The following is an example of this transformation configuration:
...
"transforms":"ExtractTopicFromValueField",
"transforms.ExtractTopicFromValueField.type":"io.aiven.kafka.connect.transforms.ExtractTopic$Value",
"transforms.ExtractTopicFromValueField.field.name":"inner_field_name",
...
PGCompatible SMT
Transformer type: io.debezium.connector.yugabytedb.transforms.PGCompatible
By default, the YugabyteDB CDC service publishes events with a schema that only includes columns that have been modified. The source connector then sends the value as null for columns that are missing in the payload. Each column payload includes a set field that is used to signal if a column has been set to null because it wasn't present in the payload from YugabyteDB.
However, some sink connectors may not understand the preceding format. PGCompatible transforms the payload to a format that is compatible with the format of the standard change data events. Specifically, it transforms column schema and value to remove the set field and collapse the payload such that it only contains the data type schema and value.
PGCompatible differs from YBExtractNewRecordState by recursively modifying all the fields in a payload.
Transaction ordering
Deprecation Notice
Starting with YugabyteDB v2024.2, and YugabyteDB gRPC Connector dz.1.9.5.yb.grpc.2024.2, the configuration transaction.ordering is deprecated. This configuration will be removed in future releases. As the PostgreSQL Logical Replication-based YugabyteDB connector offers the same transactional ordering properties by default, you are advised to use the same for your use cases.
Currently, for cases where you absolutely need to use transactional ordering with the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector, add the following configurations to use the deprecated configuration:
{
...
"transaction.ordering":"true",
"TEST.override.transaction.ordering.deprecation":"true"
...
}
In a CDC Stream, events from different transactions in different tablets across tables may appear at different times. This works well in use cases such as archiving, or with applications where only eventual consistency is required. There is another class of applications, where the end destination is another OLTP / operational database. These databases can have constraints (such as foreign keys) and strict transactional consistency requirements. In these cases, the stream of events cannot be applied as is, as events of the same transaction may appear out of order because transactions in YugabyteDB can span two tablets.
The YugabyteDB source connector supports transaction ordering, which guarantees consistent streaming of records in the sorted order based on time. With transaction ordering enabled, the connector can be used to stream change events while honoring the constraints.
To use transaction ordering, you need to set the configuration property transaction.ordering to true. Additionally, a transformer ByLogicalTableRouter is required to send all the events to a common topic to ensure that the published change events are published in the same sorted order as they are meant to be.
The following table describes properties for configuring transaction ordering.
| Property | Definition |
|---|---|
| transaction.ordering | Whether to enable ordering of transactions by their commit time. |
| transforms | Logical name for the transformer to use. For example, the following property definitions use Reroute. |
| transforms.Reroute.topic.regex | Specifies a regular expression that the transformation applies to each change event record to determine if it should be routed to a particular topic. |
| transforms.Reroute.topic.replacement | A regular expression that represents the destination topic name. |
| transforms.Reroute.type | Transformer class to be used. |
| transforms.Reroute.key.field.regex | Specifies a regular expression that the transformation applies to the default destination topic name to capture one or more groups of characters. |
| transforms.Reroute.key.field.replacement | Specifies a regular expression for determining the value of the inserted key field in terms of those captured groups. |
| provide.transaction.metadata | Whether to generate events with transaction boundaries. |
For usage example, refer to YugabyteDB CDC Consistent Streaming Pipeline in the example repository.
Transaction boundaries
The connector publishes metadata that can be used to distinguish transaction boundaries for a downstream application to implement atomicity. After the configuration property provide.transaction.metadata is enabled, the connector will also publish events indicating the beginning and end of the transaction. For more information, see Transaction metadata.
Prerequisites
- Create the Stream ID should in the
EXPLICITcheckpointing mode. For more information, see yb-admin create_change_data_stream. - You should always run the connector with a single task, that is,
tasks.maxshould always be set to 1.
Known limitations
- Transactional ordering is currently not supported with schema evolution. See issue 18476.
Monitoring
For information on monitoring CDC, refer to Monitor.
Behavior when things go wrong
Debezium is a distributed system that captures all changes in multiple upstream databases; it never misses or loses an event. When the system is operating normally or being managed carefully then Debezium provides exactly once delivery of every change event record.
If a fault does happen then the system does not lose any events. However, while it is recovering from the fault, it might repeat some change events. In these abnormal situations, Debezium, like Kafka, provides at least once delivery of change events.
The rest of this section describes how Debezium handles various kinds of faults and problems.
Configuration and startup errors
In the following situations, the connector fails when trying to start, reports an error/exception in the log, and stops running:
- The connector's configuration is invalid.
- The connector cannot successfully connect to YugabyteDB by using the specified connection parameters.
- The connector is restarting from a previously-recorded checkpoint and YugabyteDB no longer has that history available.
In these cases, the error message has details about the problem and possibly a suggested workaround. After you correct the configuration or address the YugabyteDB problem, restart the connector.
YB-TServer becomes unavailable
In case one of the tablet servers crashes, the replicas on other YB-TServer nodes will become the leader for the tablets that were hosted on the crashed server. The YugabyteDB gRPC Connector will figure out the new tablet leaders and start streaming from the checkpoint the Debezium maintains.
YugabyteDB server failures
In case of YugabyteDB server failures, the YugabyteDB gRPC Connector will try for a configurable amount of time for the availability of the YB-TServer and will stop if the cluster cannot start. When the cluster is restarted, the connector can be run again and it will start processing the changes with the committed checkpoint.
Connector unable to find table association with stream ID
In this case, the connector throws an exception with an error message that the table is not a part of the stream ID.
This can happen in the following 2 scenarios:
- The stream ID you have created might belong to any other database than the one being polled.
- The table you are asking to poll for has no primary keys on it. In this case, the table will not be a part of the stream ID. To continue, add a primary key on the table and create a new stream ID on the database.
YugabyteDB server becomes unavailable
When the connector is running, the YugabyteDB server that it is connected to could become unavailable for any number of reasons. If this happens, the connector fails with an error and stops. When the server is available again, restart the connector.
The connector externally stores the last processed offset in the form of a checkpoint. After a connector restarts and connects to a server instance, the connector communicates with the server to continue streaming from that particular offset. This offset is available as long as the stream ID remains intact. Never delete a stream ID without deleting all the associated connectors with it, otherwise you will lose data.
Dropping a table part of the replication
While the connector is running with a set of tables configured to capture the changes, if one of the tables in the set is dropped, the connector will fail with an error message indicating that the object is not found.
To avoid or resolve a failure due to a dropped table, follow these steps:
- Delete the connector that contains the table that was dropped, or that you want to drop.
- Edit the configuration and remove the given table from
table.include.list. - Deploy a new connector with the updated configuration.
Kafka Connect process stops gracefully
Suppose that Kafka Connect is being run in distributed mode and a Kafka Connect process is stopped gracefully. Prior to shutting down that process, Kafka Connect migrates the process's connector tasks to another Kafka Connect process in that group. The new connector tasks start processing exactly where the prior tasks stopped. There is a short delay in processing while the connector tasks are stopped gracefully and restarted on the new processes.
Kafka Connect process crashes
If the Kafka Connector process stops unexpectedly, any connector tasks it was running terminate without recording their most recently processed offsets. When Kafka Connect is being run in distributed mode, Kafka Connect restarts those connector tasks on other processes. However, YugabyteDB connectors resume from the last offset that was recorded by the earlier processes. This means that the new replacement tasks might generate some of the same change events that were processed just prior to the crash. The number of duplicate events depends on the offset flush period and the volume of data changes just before the crash.
Because there is a chance that some events might be duplicated during a recovery from failure, consumers should always anticipate some duplicate events. Debezium changes are idempotent, so a sequence of events always results in the same state.
In each change event record, Debezium connectors insert source-specific information about the origin of the event, including the YugabyteDB server's time of the event, the ID of the server transaction, and the position in the write-ahead log where the transaction changes were written. Consumers can keep track of this information, especially the LSN, to determine whether an event is a duplicate.
Kafka becomes unavailable
As the connector generates change events, the Kafka Connect framework records those events in Kafka by using the Kafka producer API. Periodically, at a frequency that you specify in the Kafka Connect configuration, Kafka Connect records the latest offset that appears in those change events. If the Kafka brokers become unavailable, the Kafka Connect process that is running the connectors repeatedly tries to reconnect to the Kafka brokers. In other words, the connector tasks pause until a connection can be re-established, at which point the connectors resume exactly where they left off.
Connector is stopped for a duration
If the connector is gracefully stopped, the database can continue to be used. Any changes are recorded in the YugabyteDB WAL. When the connector restarts, it resumes streaming changes where it left off. That is, it generates change event records for all database changes that were made while the connector was stopped.
A properly configured Kafka cluster is able to handle massive throughput. Kafka Connect is written according to Kafka best practices, and given enough resources a Kafka Connect connector can also handle very large numbers of database change events. Because of this, after being stopped for a while, when a Debezium connector restarts, it is very likely to catch up with the database changes that were made while it was stopped. How quickly this happens depends on the capabilities and performance of Kafka and the volume of changes being made to the data in YugabyteDB.