Python Drivers YSQL
Yugabyte Psycopg2 smart driver is a Python driver for YSQL built on the PostgreSQL psycopg2 driver, with additional connection load balancing features.
For more information on the YugabyteDB psycopg2 smart driver, see the following:
Download the driver dependency
Building Psycopg2 requires a few prerequisites (a C compiler and some development packages). Check the installation instructions and the FAQ for details.
The YugabyteDB Psycopg2 driver requires PostgreSQL version 12 or later (preferably 14).
If prerequisites are met, you can install psycopg2-yugabytedb like any other Python package, using pip to download it from PyPI:
$ pip install psycopg2-yugabytedb
Or, you can use the setup.py script if you've downloaded the source package locally:
$ python setup.py build
$ sudo python setup.py install
Fundamentals
Learn how to perform common tasks required for Python application development using the YugabyteDB Psycopg2 smart driver.
Load balancing connection properties
The following connection properties need to be added to enable load balancing:
load_balance- enable cluster-aware load balancing by setting this property to one of the allowed values other thanfalse; disabled by default.topology_keys- provide comma-separated geo-location values to enable topology-aware load balancing. Geo-locations can be provided ascloud.region.zone.
By default, the driver refreshes the list of nodes every 300 seconds (5 minutes). You can change this value by including the yb_servers_refresh_interval parameter.
For more information, see Cluster-aware load balancing.
Use the driver
To use the driver, pass new connection properties for load balancing in the connection string or in the dictionary.
To enable uniform load balancing across all servers, you set the load_balance property to true or any in the connection string or dictionary, as per the following examples:
-
Connection String
conn = psycopg2.connect("dbname=database_name host=hostname port=5433 user=username password=password load_balance=true") -
Connection Dictionary
conn = psycopg2.connect(user = 'username', password='password', host = 'hostname', port = '5433', dbname = 'database_name', load_balance='True')
You can specify multiple hosts in the connection string in case the primary address fails. After the driver establishes the initial connection, it fetches the list of available servers from the cluster, and load-balances subsequent connection requests across these servers.
To specify topology keys, you set the topology_keys property to comma-separated values in the Connection string or dictionary, as per the following examples:
-
Connection String
conn = psycopg2.connect("dbname=database_name host=hostname port=5433 user=username password=password load_balance=true topology_keys=cloud.region.zone1,cloud.region.zone2") -
Connection Dictionary
conn = psycopg2.connect(user = 'username', password='password', host = 'hostname', port = '5433', dbname = 'database_name', load_balance='True', topology_keys='cloud.region.zone1,cloud.region.zone2')
To configure a SimpleConnectionPool, specify load balance as follows:
yb_pool = psycopg2.pool.SimpleConnectionPool(1, 10, user="yugabyte",
password="yugabyte",
host="127.0.0.1",
port="5433",
database="yugabyte",
load_balance="True")
conn = yb_pool.getconn()
Try it out
This tutorial shows how to use the Yugabyte Psycopg2 driver with YugabyteDB. It starts by creating a 3 node cluster with a replication factor of 3. This tutorial uses the yb-ctl utility.
Next, you use a Python shell terminal to demonstrate the driver's load balancing features by running a few python scripts.
Note
The driver requires YugabyteDB version 2.7.2.0 or later.Create a local cluster
Create a universe with a 3-node RF-3 cluster with some fictitious geo-locations assigned. The placement values used are just tokens and have nothing to do with actual AWS cloud regions and zones.
cd <path-to-yugabytedb-installation>
To create a multi-zone cluster, do the following:
-
Start the first node by running the yugabyted start command, passing in the
--cloud_locationand--fault_toleranceflags to set the node location details, as follows:./bin/yugabyted start --advertise_address=127.0.0.1 \ --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node1 \ --cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a \ --fault_tolerance=zone -
Start the second and the third node on two separate VMs using the
--joinflag, as follows:./bin/yugabyted start --advertise_address=127.0.0.2 \ --join=127.0.0.1 \ --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node2 \ --cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a \ --fault_tolerance=zone./bin/yugabyted start --advertise_address=127.0.0.3 \ --join=127.0.0.1 \ --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node3 \ --cloud_location=aws.us-east-1.us-east-1b \ --fault_tolerance=zone
Check uniform load balancing
Log into your Python terminal and run the following script:
import psycopg2
conns = []
for i in range(30):
conn = psycopg2.connect(user = 'username', password='xxx', host = 'hostname', port = '5433', dbname = 'database_name', load_balance='True')
conns.append(conn)
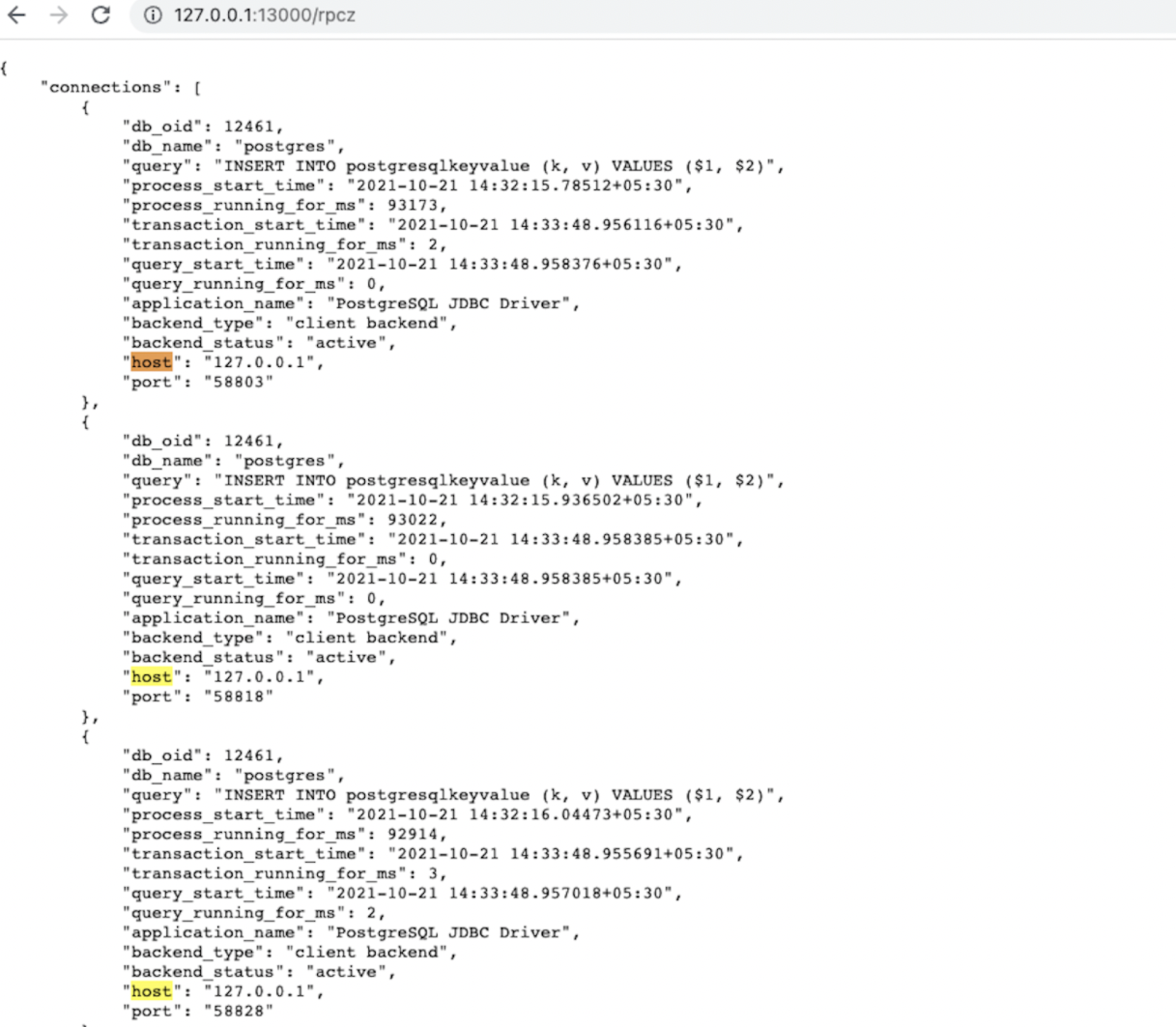
The application creates 30 connections. To verify the behavior, wait for the app to create connections and then visit http://<host>:13000/rpcz from your browser for each node to see that the connections are equally distributed among the nodes. This URL presents a list of connections where each element of the list has some information about the connection as shown in the following screenshot. You can count the number of connections from that list, or search for the occurrence count of the host keyword on that webpage. Each node should have 10 connections.
You can also verify the number of connections by running the following script in the same terminal:
from psycopg2.policies import ClusterAwareLoadBalancer as lb
obj = lb()
obj.printHostToConnMap()
This displays a key value pair map where the keys are the host and the values are the number of connections on them. (This is the client-side perspective of the number of connections.)
Check topology-aware load balancing using yb-sample-apps
Run the following script in your new Python terminal with the topology_keys property set to aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a; only two nodes are used in this case.
import psycopg2
conns = []
for i in range(30):
conn = psycopg2.connect(user = 'username', password='xxx', host = 'hostname', port = '5433', dbname = 'database_name', load_balance='True', topology_keys='aws.us-east-1.us-east-1a')
conns.append(conn)
To verify the behavior, wait for the app to create connections and then navigate to http://<host>:13000/rpcz. The first two nodes should have 15 connections each, and the third node should have zero connections. You can also verify this by running the previous verify script in the same terminal.
Clean up
When you're done experimenting, run the following command to destroy the local cluster:
./bin/yugabyted destroy --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node1
./bin/yugabyted destroy --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node2
./bin/yugabyted destroy --base_dir=$HOME/yugabyte-2.23.1.0/node3
Limitations
Currently, PostgreSQL psycopg2 driver and Yugabyte Psycopg2 smart driver cannot be used in the same environment.