Use Gitpod workspaces to provision an instant development environment with a pre-configured YugabyteDB.
Gitpod is a configurable ready-to-code cloud development environment accessible via a browser. A Gitpod workspace includes everything you need to develop for a specific repository, including the Visual Studio Code editing experience, common languages, tools, and utilities. Instantly this sets up a cloud-hosted, containerized, and customizable editing environment.
Follow the steps on this page to set up a Gitpod workspace environment with a pre-configured YugabyteDB. For details on Gitpod workspaces, refer to the Gitpod documentation.
Requirements
Gitpod doesn't require anything on your local computer other than a code editor and Git CLI. Much of the development happens in the cloud through a web browser.
Get started with a boot app
You can find the source at Spring Boot todo on GitHub.
The easy way to get started with Gitpod is to simply fork this source repository and initialize the Gitpod workspace environment by invoking https://gitpod.io/#[REPO_URL] in a browser window. Replace [REPO_URL] with your forked repository URL and you should already have been connected to the Gitpod account before launching the browser URL.
If you want to set up the Spring Boot app from scratch, use the following instructions to bootstrap the base project template and copy the appropriate files and content from the source repository.
Initialize the base project structure
Spring todo is a Java Spring Boot reactive app. However, the steps to go through the Gitpod experience are language- and framework-agnostic. A quick way to get started with a Spring Boot app is via the Spring Initializer. Generate the base project structure with Webflux, Flyway, and R2DBC dependencies.
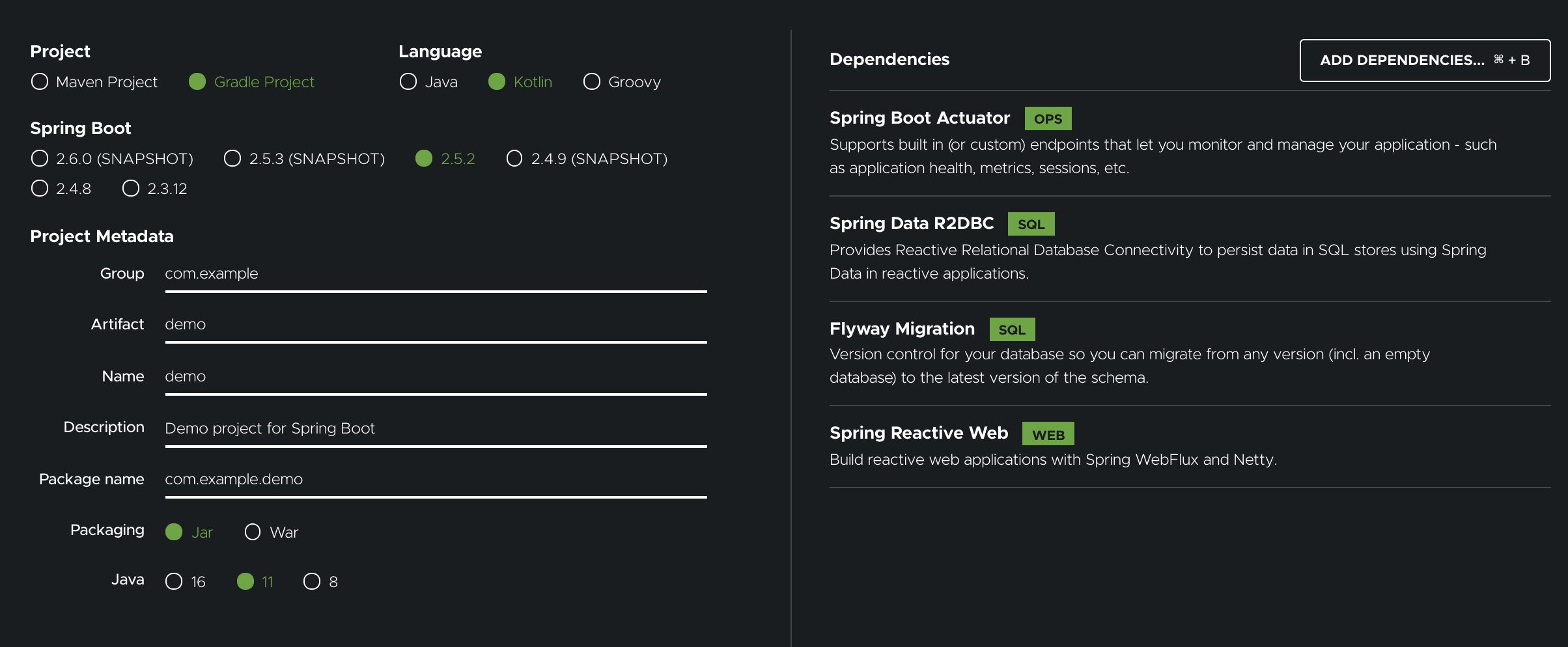
Complete the CRUD APIs
Complete the todo-service by copying the source and build files from the source repository to your own repository to handle GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE API requests.
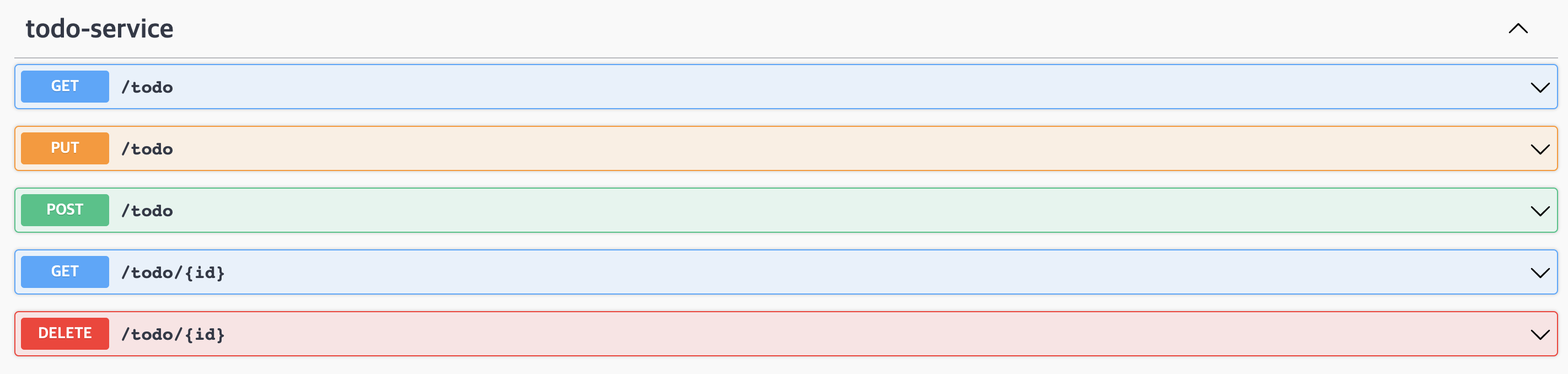
Note
The application uses non-blocking reactive APIs to connect to YugabyteDB.Initialize Gitpod
To get started quickly, you can use the universal image pre-built containers or a language-specific image. These can be further customized to fit your needs either by extending them or by creating a new one. A single click provisions the entire development environment in the cloud with an integrated powerful Visual Studio Code editor. The entire configuration to set up the development environment lives in the same source code repository. Follow the steps in the next sections to set up and customize your Gitpod environment.
Set up the Gitpod environment
You initialize the Gitpod workspace environment for a specific repository by invoking https://gitpod.io/#[REPO_URL].
You can either use a universal image with pre-configured libraries and commonly used utilities or a language-specific image. Create the integrated YugabyteDB workspace environment by customizing the base universal image. Use the editor in your Gitpod environment to add these files directly and commit them back to your GitHub repository.
To initialize the workspace environment:
- create a
.gitpod.ymlfile at the root of the source repository - create a
.gitpodcontainerfolder at the root of the source repository to hold the customizedDockerfile
Customize the Gitpod environment
You need to customize the default universal image to include the YugabyteDB binary. You do this by defining your own Dockerfile at .gitpodcontainer/Dockerfile. Refer to the source repository for the complete file.
# default universal image
FROM gitpod/workspace-full
ARG YB_VERSION=2.7.1.1
ARG ROLE=gitpod
USER root
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
netcat --no-install-recommends
# download and initialize the file structure
RUN curl -sSLo ./yugabyte.tar.gz https://downloads.yugabyte.com/yugabyte-${YB_VERSION}-linux.tar.gz \
&& mkdir yugabyte \
&& tar -xvf yugabyte.tar.gz -C yugabyte --strip-components=1 \
&& mv ./yugabyte /usr/local/ \
&& ln -s /usr/local/yugabyte/bin/yugabyted /usr/local/bin/yugabyted \
&& ln -s /usr/local/yugabyte/bin/ysqlsh /usr/local/bin/ysqlsh \
&& chmod +x /usr/local/bin/yugabyted \
&& chmod +x /usr/local/bin/ysqlsh \
&& rm ./yugabyte.tar.gz
RUN mkdir -p /var/ybdp \
&& chown -R $ROLE:$ROLE /var/ybdp \
&& chown -R $ROLE:$ROLE /usr/local/yugabyte
USER $ROLE
The following lines of code write the app-specific database information to a local file that will be run during the container initialization phase.
ENV STORE=/var/ybdp
ENV LISTEN=127.0.0.1
ENV PORT=5433
RUN echo "CREATE DATABASE todo;" > $STORE/init-db.sql \
&& echo "CREATE USER todo WITH PASSWORD 'todo';" >> $STORE/init-db.sql \
&& echo "GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE todo TO todo;" >> $STORE/init-db.sql \
&& echo '\\c todo;' >> $STORE/init-db.sql \
&& echo "CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS \"uuid-ossp\";" >> $STORE/init-db.sql
To initialize the workspace launch environment, customize the .gitpod.yml file as follows:
# Refer the customized docker image
image:
file: .gitpodcontainer/Dockerfile
# Run the app and db related jobs
# - run the db post-init script
# - start the DB instance
# - run the db app specific init script
# - build and run the app process
tasks:
- name: db-run
before: /usr/local/yugabyte/bin/post_install.sh
init: |
yugabyted start --base_dir=$STORE/ybd1 --listen=$LISTEN && \
[[ ! -f $STORE/.init-db.sql.completed ]] && { for i in {1..10}; do (nc -vz $LISTEN $PORT >/dev/null 2>&1); [[ $? -eq 0 ]] && { ysqlsh -f $STORE/init-db.sql; touch $STORE/.init-db.sql.completed; break; } || sleep $i; done } && \
[[ ! -f $STORE/.init-db.sql.completed ]] && echo 'YugabyteDB is not running!'
- name: app-run
init: gradle clean build -x test
command: java -jar build/libs/*.jar
ports:
- port: 8080
onOpen: notify
- port: 7000
onOpen: notify
- port: 9000
onOpen: notify
- port: 37843
onOpen: ignore
- port: 7100
onOpen: ignore
- port: 9100
onOpen: ignore
- port: 5433
onOpen: ignore
- port: 13000
onOpen: ignore
- port: 9042
onOpen: ignore
- port: 12000
onOpen: ignore
Commit Dockerfile and .gitpod.yml to your GitHub repository.
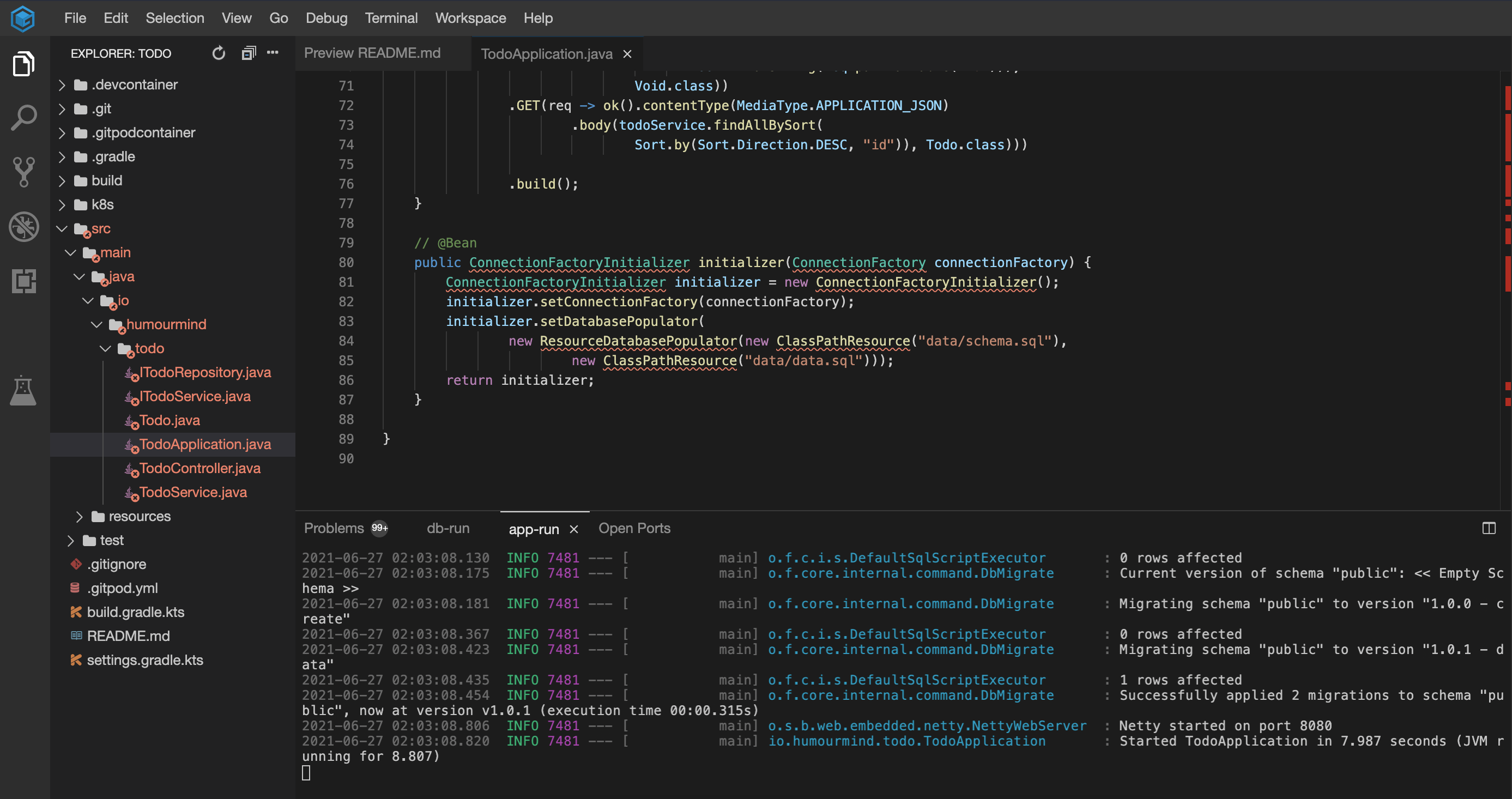
Next, launch the workspaces environment again with this updated spec to provision the development environment with a running YugabyteDB instance. This opens two terminals; one terminal runs the DB task, and the other compiles and runs the boot app.
Gitpod provisions a fully integrated ready-to-code cloud-native development environment with automated port forwarding to develop, build, and test applications right in your browser.
Summary
Gitpod provides fully automated, pre-configured, and consistent development environments that improve the productivity of distributed teams.