Global and geo-local tables
Depending on your business needs, you might want to have some data available across multiple geographies and some data in specific geographies due to local laws. You can accomplish this need using several patterns like Global Database, Locality-optimized Geo-partition, and Follower Reads.
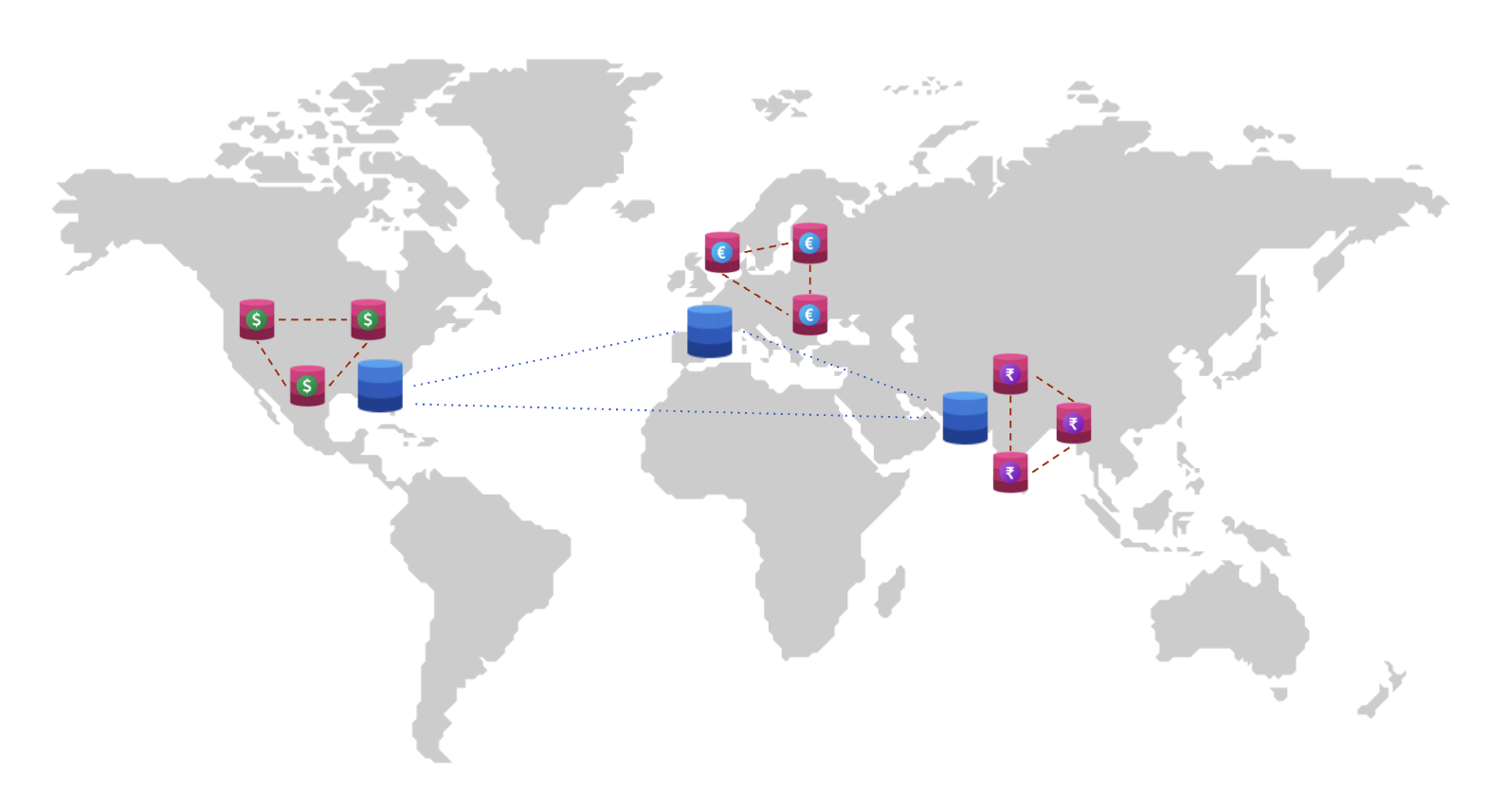
Suppose that your business sells products in multiple geographies, say the USA, Europe, and the Indian subcontinent. You need to have your product catalog available in all of the geographies but have to keep your customers order information local to the geo for GDPR. At the same time, you need to serve all data with low latency.
Setup
Setup
To set up a local universe, refer to Set up a local YugabyteDB universe.Setup
To set up a cluster, refer to Set up a YugabyteDB Aeon cluster.Setup
To set up a universe, refer to Set up a YugabyteDB Anywhere universe.Set up a 3 region RF3 cluster as you need the cluster to be spread across 3 geographies, the US, Europe, and India.
Global catalog data
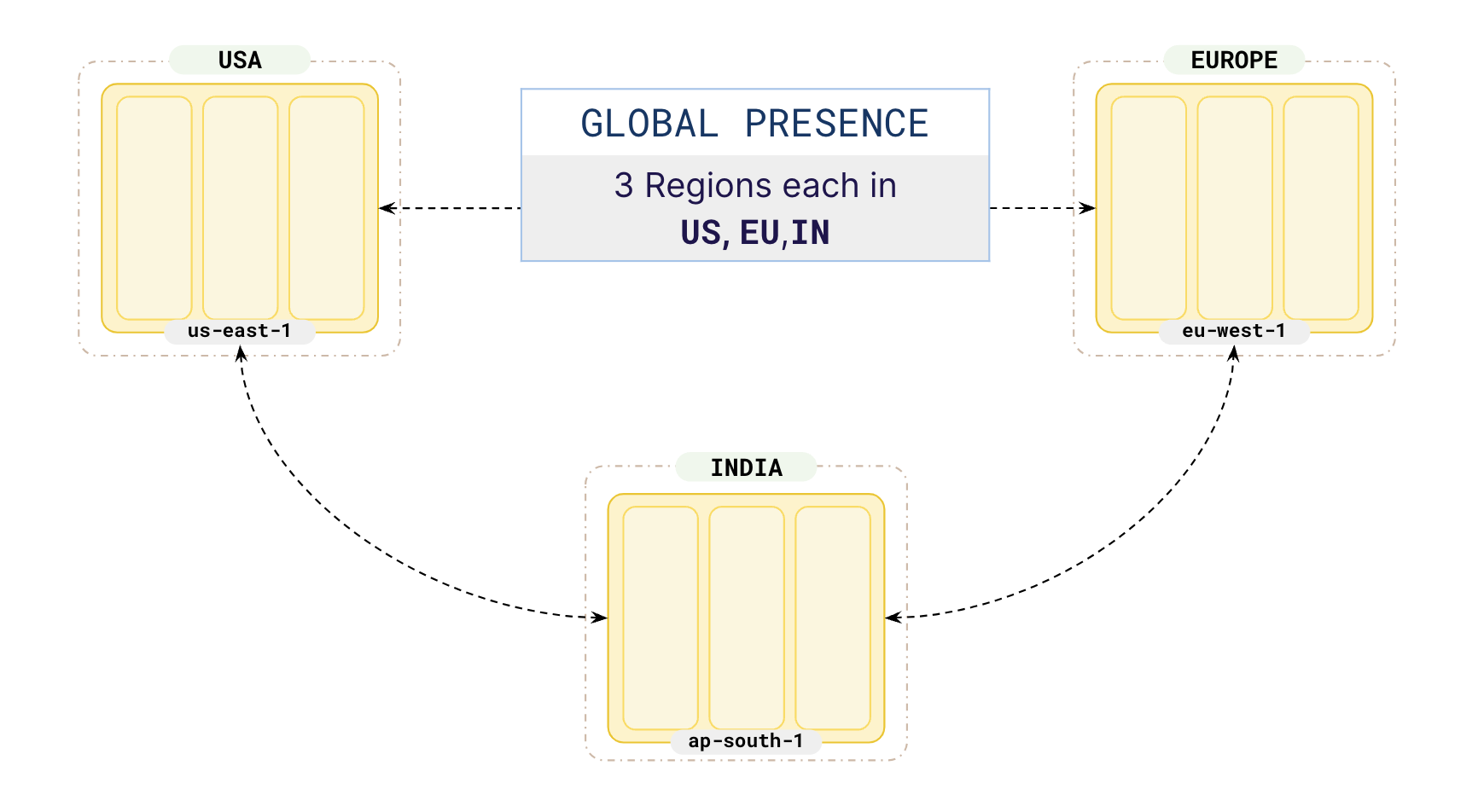
Start by creating two tables, catalog and orders, where the catalog table is a global table distributed across the USA, Europe and India while the orders table is to be partitioned to keep data local in each geo.
To place the catalog table globally , you need to create a global tablespace that spreads across the three geos as follows:
-- tablespace for Global data
CREATE TABLESPACE global WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-1","zone":"eu-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1}
]}'
);
orders table. It is important to note that all tables are global by default.
catalog table, it is recommended to set the leader preference to the region where the application that updates the catalog table runs, or where most of your users are located.Next, create the catalog table and attach it to the global tablespace to ensure that the catalog table is placed in all 3 geos.
CREATE TABLE catalog (
id INTEGER NOT NULL, /* product id */
name VARCHAR NOT NULL, /* product name */
price DECIMAL NOT NULL, /* base price */
) TABLESPACE global;
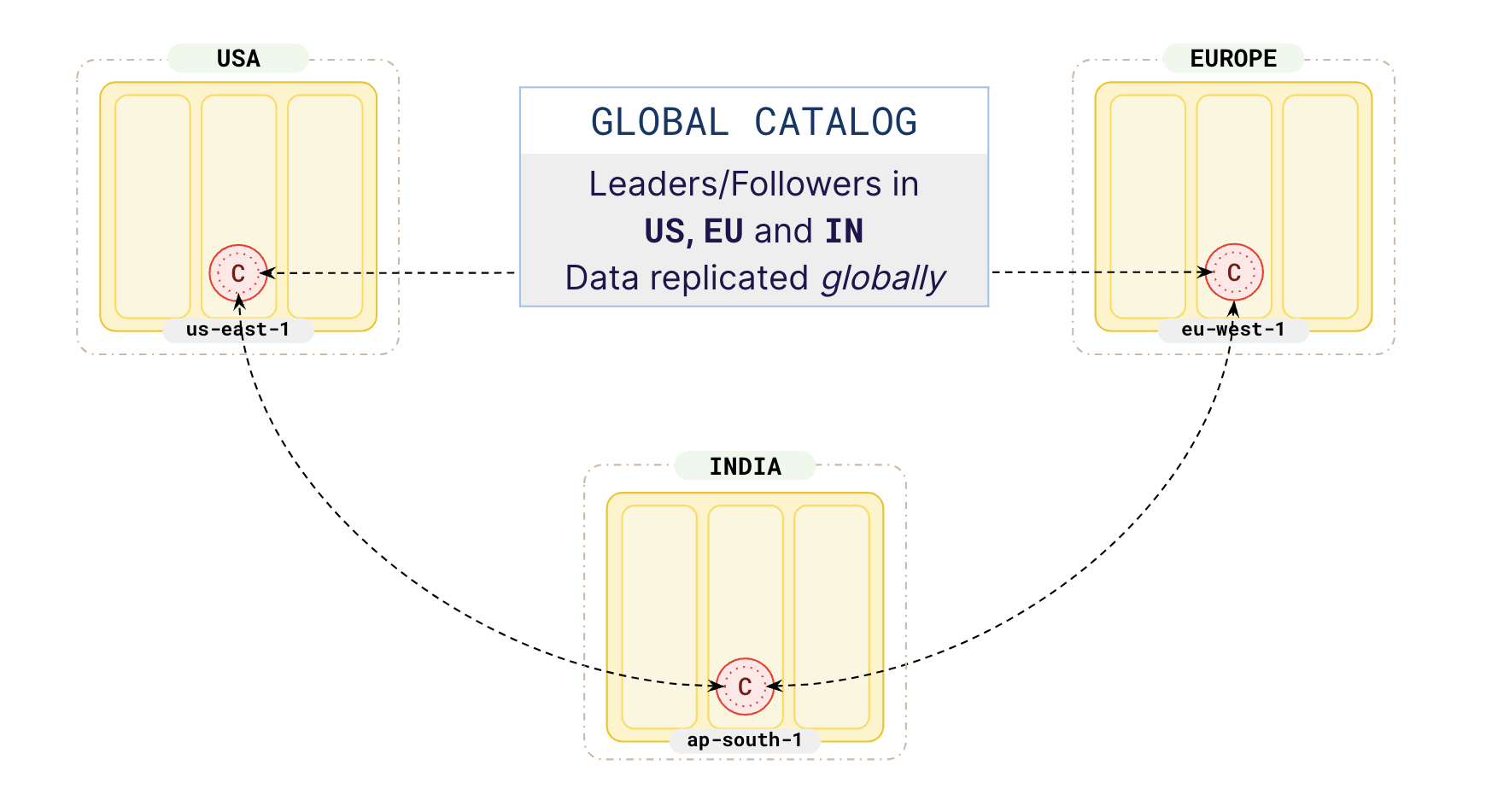
Local orders
Create a table of orders that you are going to partition by the geo field.
CREATE TABLE orders (
orderid INTEGER NOT NULL,
userid INTEGER NOT NULL,
productid INTEGER NOT NULL,
price DECIMAL NOT NULL, /* sale price */
geo VARCHAR,
) PARTITION BY LIST (geo);
Before you partition the orders table, create the correct tablespaces so that you can correctly place the partitions.
Tablespaces for partition placement
Configure your us orders to be placed in us-east-1, with one replica in each of the zones (us-east-[1a/1b/1c]). Placing the replicas in the same region as the leader ensures that the local replica is up-to-date and will be quickly promoted to leader in case the current leader fails. This way, all the replicas of the US orders are located in the US regions.
-- tablespace for us data
CREATE TABLESPACE us WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1b","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1c","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1}
]}'
);
Similarly, set up your europe partitions in eu-west-1.
-- tablespace for Europe data
CREATE TABLESPACE eu WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-1","zone":"eu-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-1","zone":"eu-west-1b","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-1","zone":"eu-west-1c","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1}
]}'
);
Similarly, set up your india partitions in ap-south-1.
-- tablespace for India data
CREATE TABLESPACE india WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1b","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"ap-south-1","zone":"ap-south-1c","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1}
]}'
);
Partitioning your data
Partition your data for users in the US, Europe, and India and attach the partitions to the above created tablespaces so that the user data of users reside in their respective geos.
-- US partition table
CREATE TABLE us PARTITION OF orders (
orderid, productid, userid, price, geo, PRIMARY KEY (orderid HASH, geo)
) FOR VALUES IN ('us') TABLESPACE us;
-- Europe partition table
CREATE TABLE eu PARTITION OF orders (
orderid, productid, userid, price, geo, PRIMARY KEY (orderid HASH, geo)
) FOR VALUES IN ('eu') TABLESPACE eu;
-- India partition table
CREATE TABLE india PARTITION OF orders (
orderid, productid, userid, price, geo, PRIMARY KEY (orderid HASH, geo)
) FOR VALUES IN ('in') TABLESPACE india;
Your orders partitions should look as described in the following illustration:
Low latency for all users
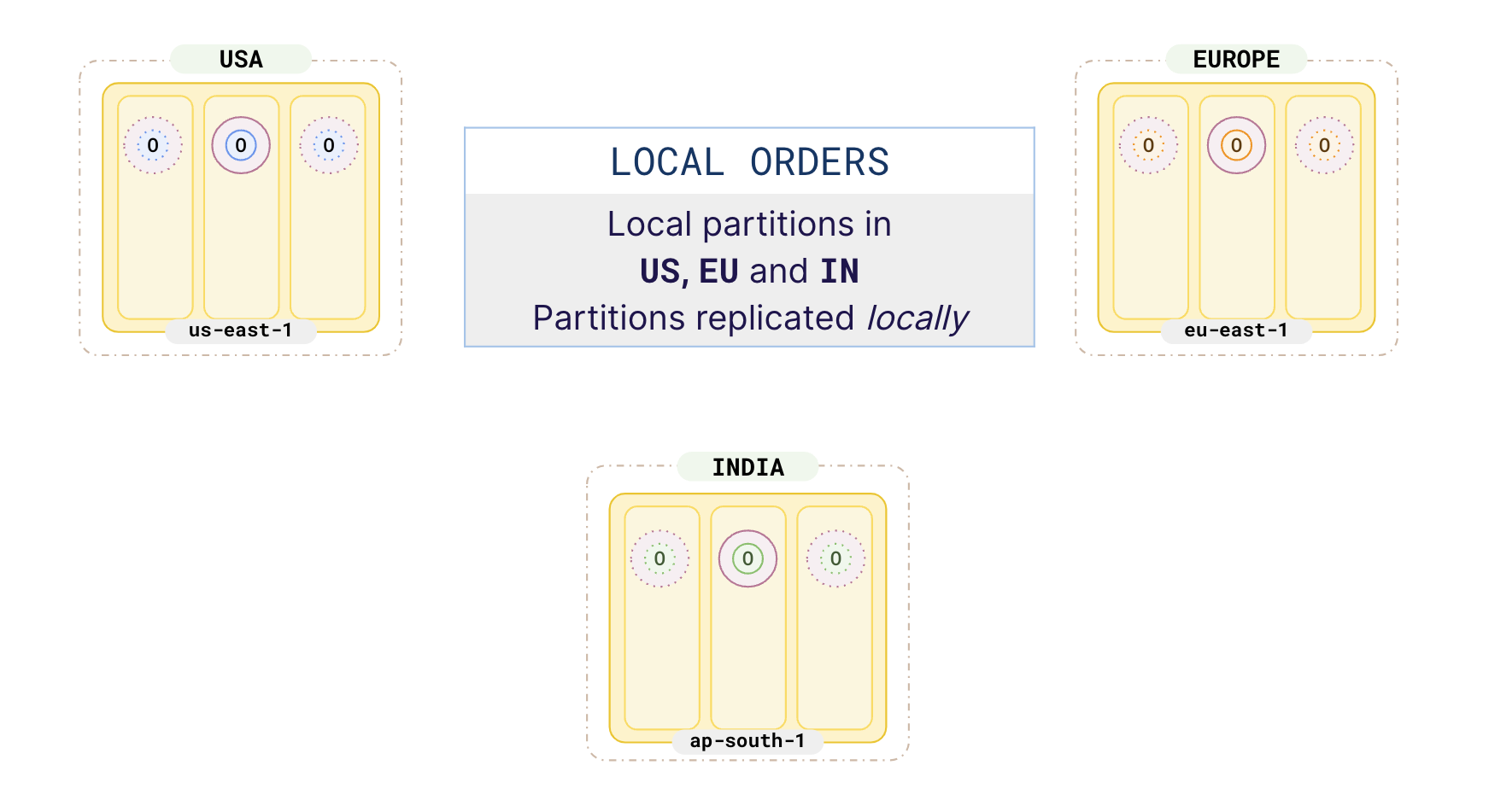
Your catalog table should span across all the 3 geos and the orders table partitioned in each of the 3 geos as per the following illustration.
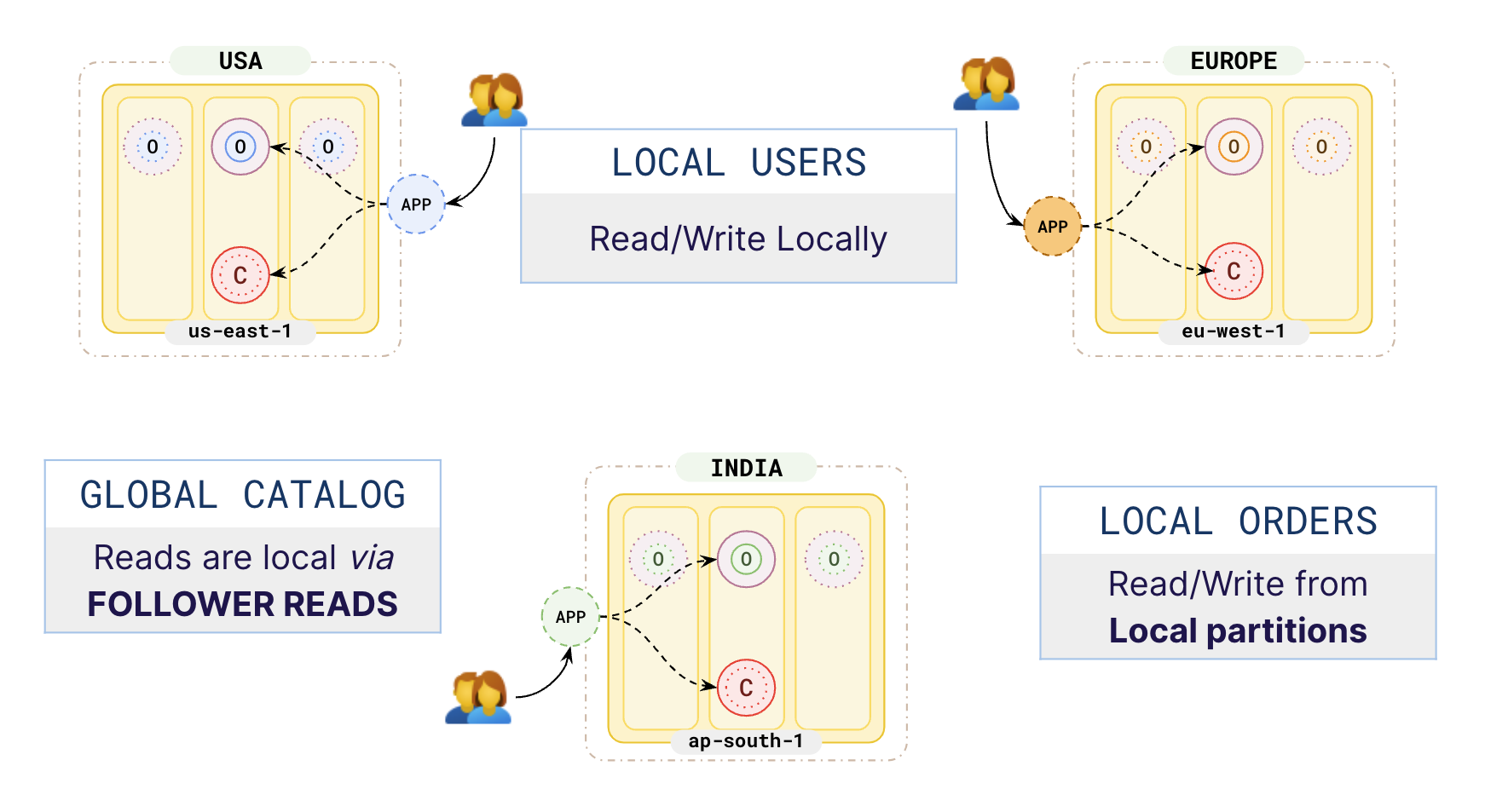
Applications in each region only access the data locally. Their orders are stored and replicated locally in their geo as the orders table is partitioned by geo. This enables fast reads and writes locally. The catalog table is globally distributed across 3 regions and does not change much, and is not directly updated by the user facing applications. So, applications can read the catalog data quickly from the followers using Follower reads.
This pattern helps applications running in different regions to have low read and write latency, as they are reading and writing data to nearby partitions. At the same time, you are complying with local data protection laws by keeping the citizen data inside the country boundaries.