Locality-optimized geo-partitioning
Data residency laws (such as the GDPR) require data of citizens or residents to be collected, processed, and stored inside the country. Multi-national businesses must operate under local data regulations that dictate how the data of a nation's residents must be stored inside its borders. Re-architecting your storage layer and applications to support these regulations could be a very daunting task.
Suppose you want to store data of users from different countries (for example, US, Germany, India) in the same table. To comply with national data-protection laws, or to reduce latency for the users in those countries, you can store the rows in their respective regions, similar to the following illustration.
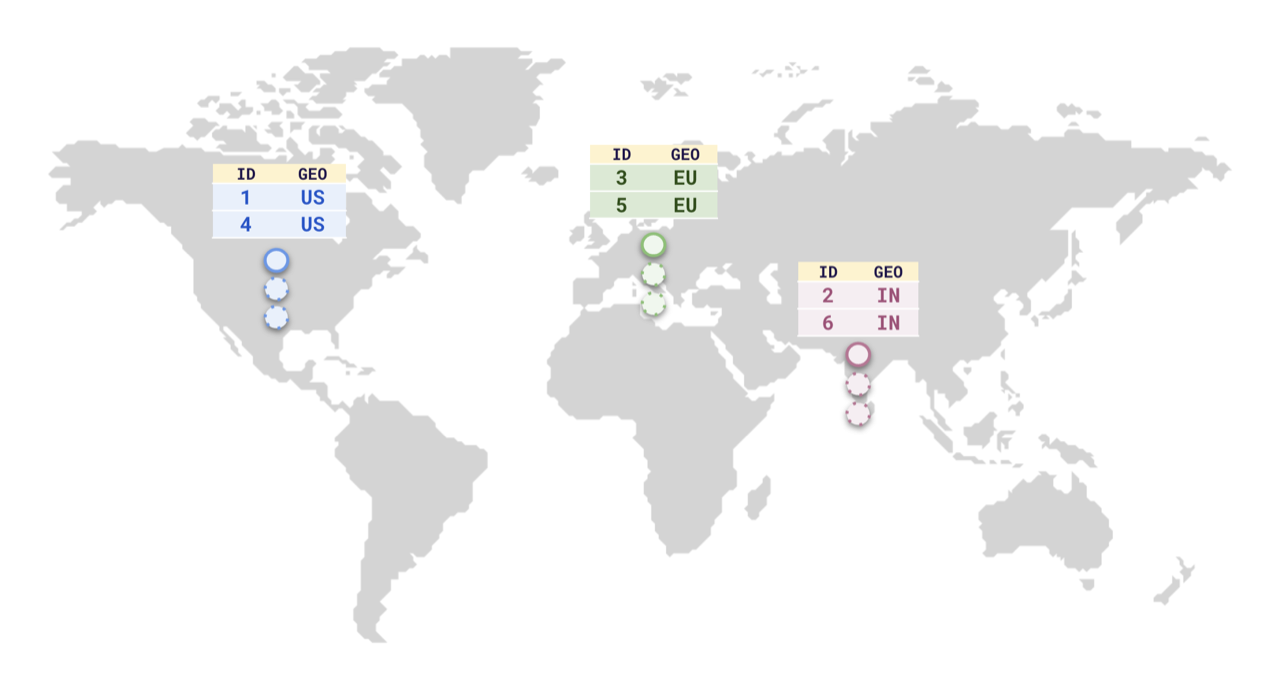
To do this, YugabyteDB supports Row-level geo-partitioning. This combines two well-known PostgreSQL concepts, partitioning, and tablespaces.
Setup
Setup
To set up a local universe, refer to Set up a local YugabyteDB universe.Setup
To set up a cluster, refer to Set up a YugabyteDB Aeon cluster.Setup
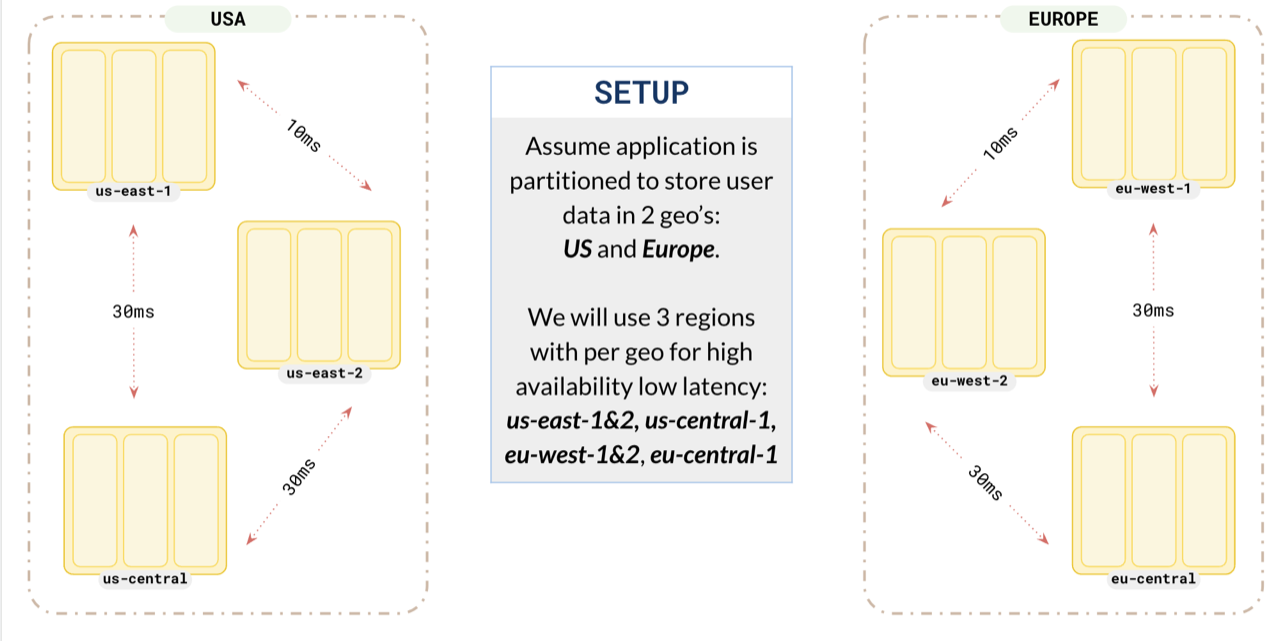
To set up a universe, refer to Set up a YugabyteDB Anywhere universe.Suppose you want to store the data of users from the US and Europe on their respective continents. For this, you set up a replication factor 3 cluster spread across 2 geographies, US and Europe. To make sure each partition acts like a global database, you opt for 3 regions in each of the geographies.
Partition your data
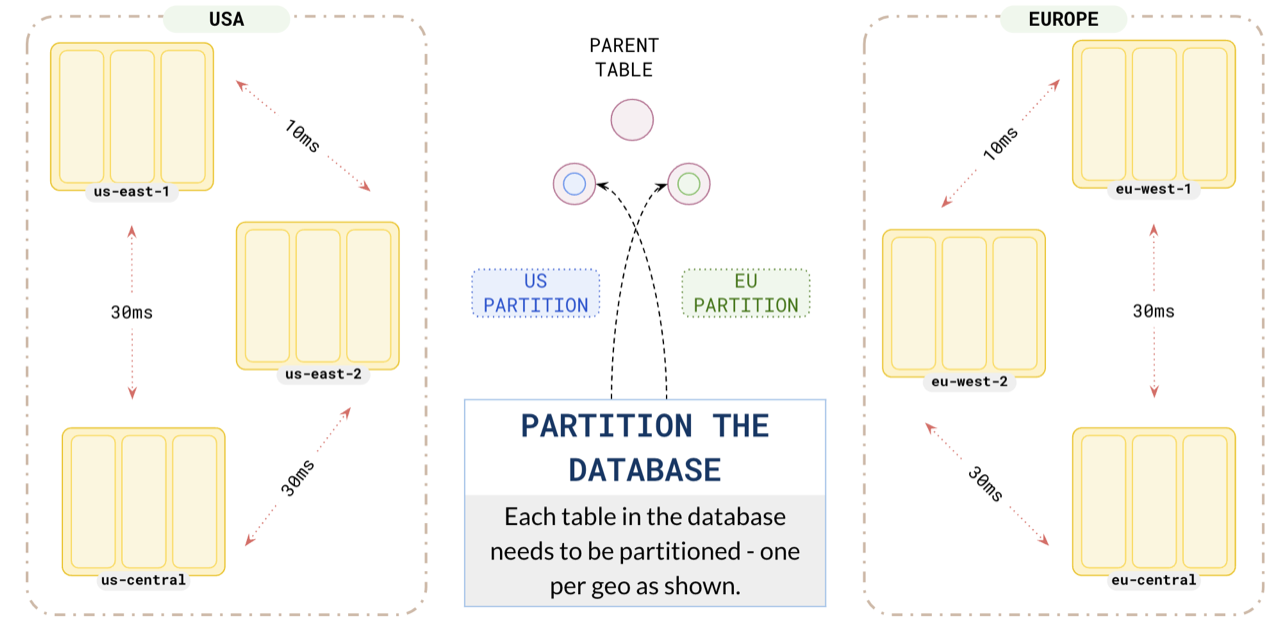
For this example, create a table of users that you are going to partition by the geo field.
CREATE TABLE users (
id INTEGER NOT NULL,
geo VARCHAR,
) PARTITION BY LIST (geo);
Partition your data for users in the US and Europe to ensure that the application in us-east uses the us partition, and the application in eu-west uses the europe partition.
-- US partition table
CREATE TABLE us PARTITION OF users (
id, geo, PRIMARY KEY (id HASH, geo)
) FOR VALUES IN ('us') TABLESPACE us;
-- Europe partition table
CREATE TABLE eu PARTITION OF users (
id, geo, PRIMARY KEY (id HASH, geo)
) FOR VALUES IN ('eu') TABLESPACE eu;
Replica placement
Configure your us partition leader preference to place the leader in us-east-1, one replica in us-east-1 (nearby region) and the other replica in us-east-2. Placing one replica in the same region as the leader ensures that the local replica is up-to-date and will be quickly promoted to leader in case the leader fails. This way , all the replicas of the US users are located in the US regions.
-- tablespace for us data
CREATE TABLESPACE us WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-1","zone":"us-east-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-east-2","zone":"us-east-1c","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":2},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"us-central-1","zone":"us-east-2b","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":3}
]}'
);
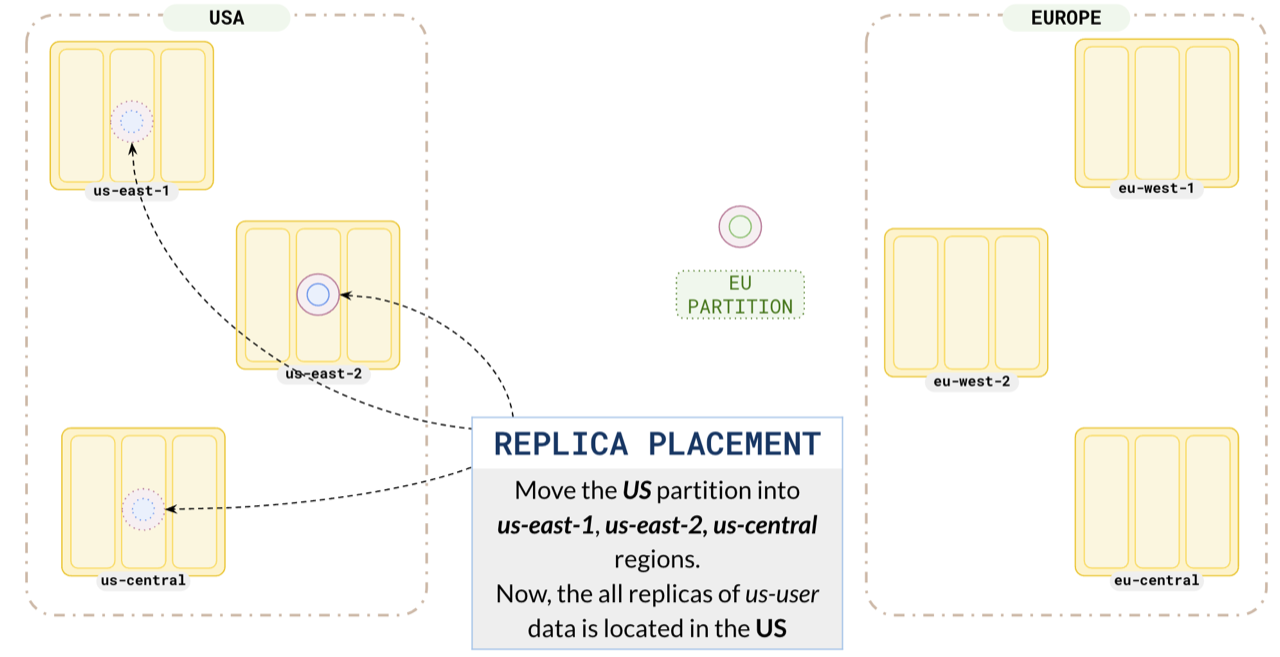
Similarly, set up your europe partitions in eu-west-1 and eu-west-2.
-- tablespace for Europe data
CREATE TABLESPACE eu WITH (
replica_placement='{"num_replicas": 3,
"placement_blocks":[
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-1","zone":"eu-west-1a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":1},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-west-2","zone":"eu-west-1c","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":2},
{"cloud":"aws","region":"eu-central-1","zone":"eu-west-2a","min_num_replicas":1,"leader_preference":3}
]}'
);
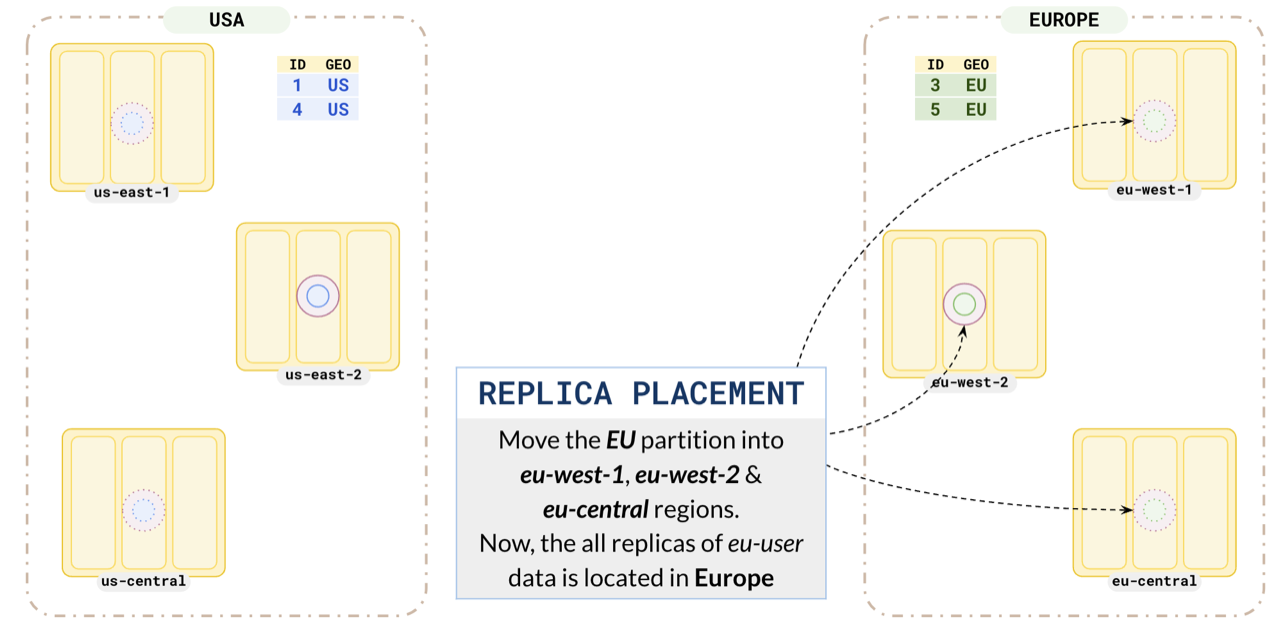
This ensures all the EU user data is located in Europe.
Low latency
Consider the US application. As you have placed the us partition leader in us-east-1, it has a low read latency of 2ms. As this partition has a replica in a nearby region, the write latency is also low (<10ms).
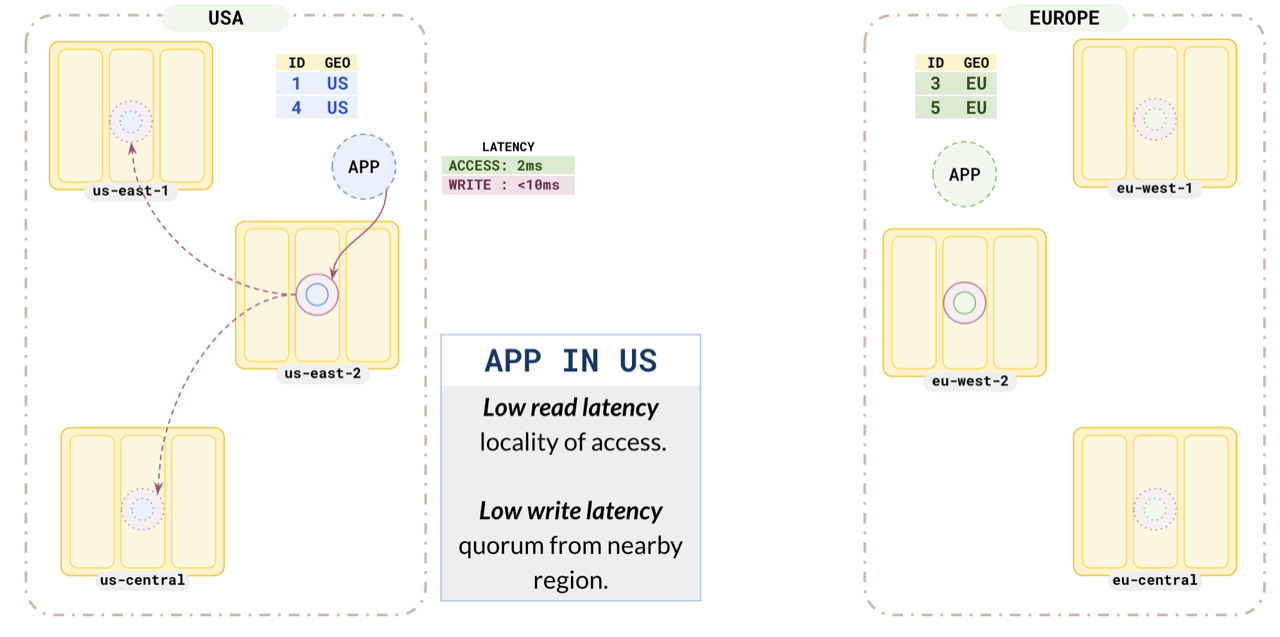
Similarly, the Europe application also has low read and write latencies.
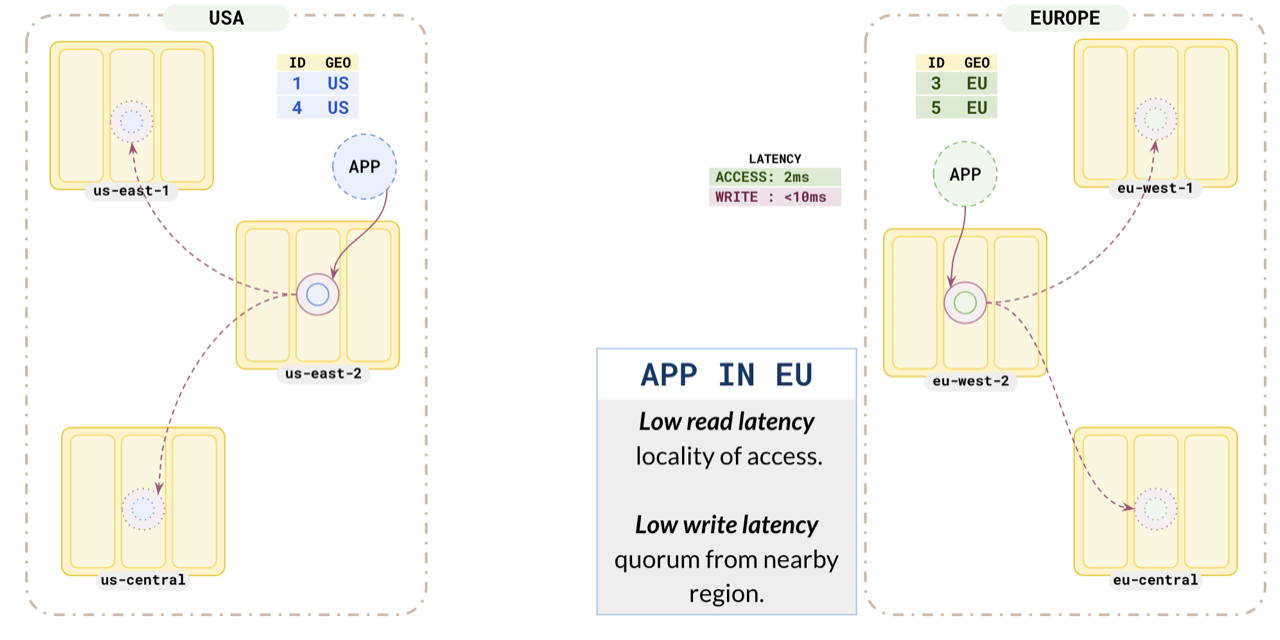
This pattern helps applications running in different regions to have low read and write latency, as they are reading and writing data to nearby partitions. At the same time, you are complying with local data protection laws by keeping the citizen data inside the country boundaries.
Global tables
You can add other tables without partitioning to be present across both geographies. This way, you can have both global tables and partitioned tables in your setup.
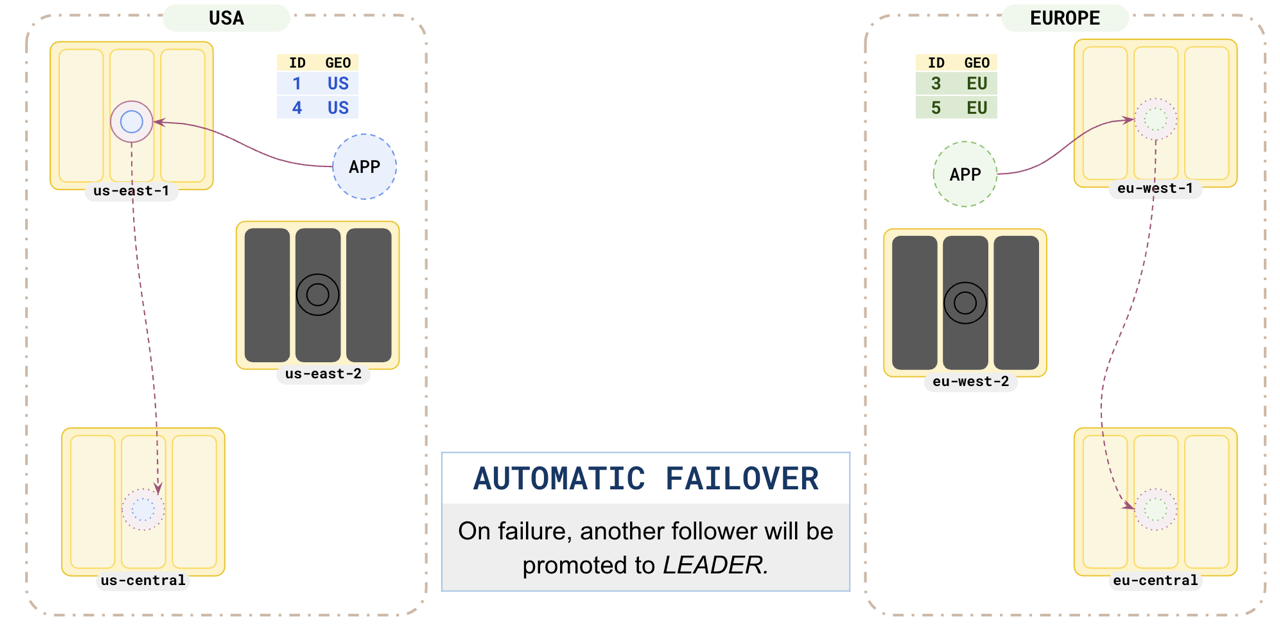
Failover
This pattern is resilient to region failure. When any of the regions hosting one of the partition leaders fails, the partition follower in another zone would immediately be promoted to leader and the application can continue without any data loss.