YB-Master service
The YB-Master service keeps the system metadata and records, such as tables and the location of their tablets, users and roles with their associated permissions, and so on.
The YB-Master service is also responsible for coordinating background operations, such as load-balancing or initiating replication of under-replicated data, as well as performing a variety of administrative operations such as creating, altering, and dropping tables.
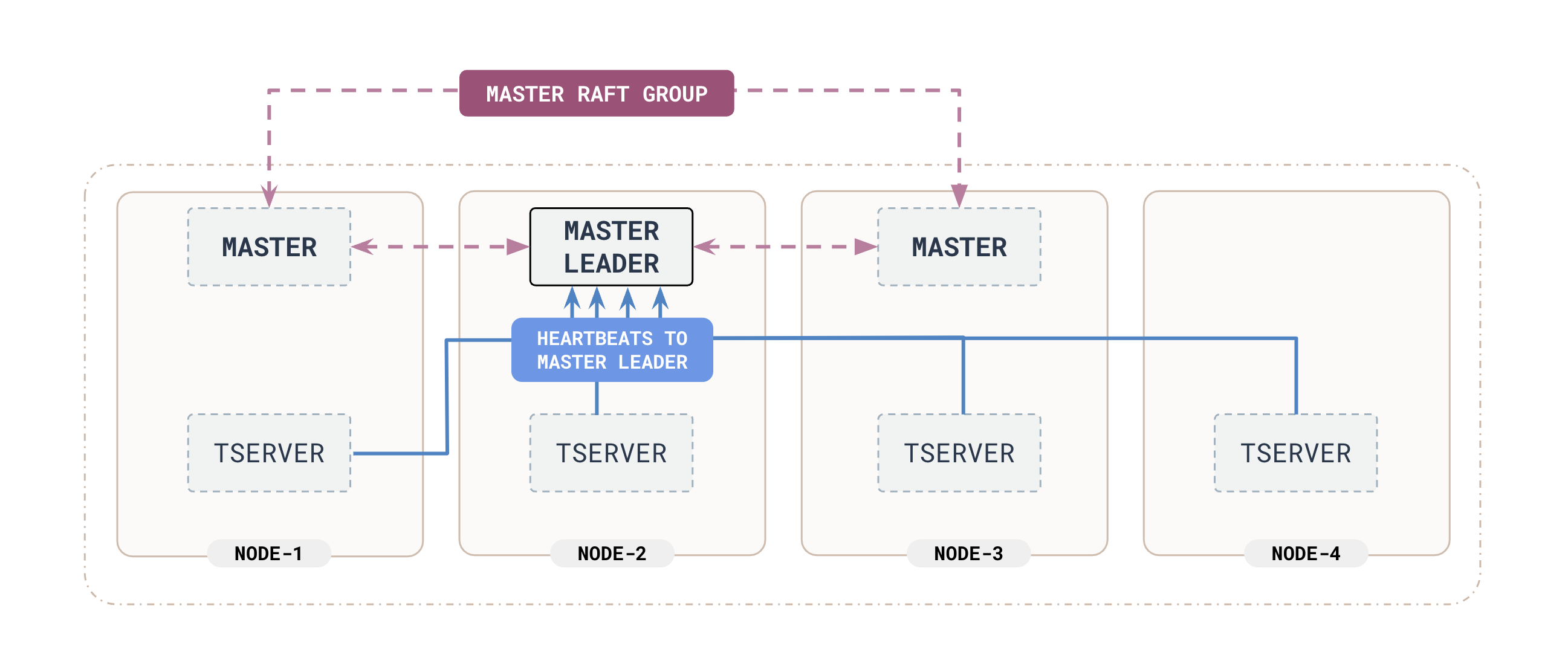
The YB-Master is highly available, as it forms a Raft group with its peers, and it is not in the critical path of I/O against user tables.
The YB-Master performs a number of important operations within the system. Some operations are performed throughout the lifetime of the universe, in the background, without impacting foreground read and write performance.
Administrative operations
When one of these universe-wide operations is initiated, such as creating a new table, modifying an existing table, dropping (deleting) a table, or creating backups, the YB-Master ensures that the operation is successfully propagated and applied to all relevant tablets, regardless of the current state of the YB-TServer nodes hosting those tablets.
This guarantee is crucial because if a YB-TServer fails while such an operation is in progress, it cannot cause the operation to be only partially applied, leaving the database in an inconsistent state. The YB-Master makes sure the operation is either fully applied everywhere or not applied at all, maintaining data integrity.
System metadata
The YB-Master stores important system-wide metadata, which includes information about:
- Namespaces (database names)
- Table information
- User roles and permissions
This system metadata is crucial for managing and coordinating the entire YugabyteDB cluster. The YB-Master stores this system metadata in an internal table. This allows the metadata to be managed and accessed like any other table in the database.
To ensure redundancy and prevent data loss, the system metadata is replicated across all YB-Master nodes using a replication protocol called Raft. This means that if one YB-Master fails, the others will still have the up-to-date system metadata.
Table creation
The YB-Master leader validates the table schema and decides the desired number of tablets for the table and creates metadata for each of them. The table schema and the tablet metadata information is replicated to YB-Master Raft group. This ensures that the table creation can succeed even if the current YB-Master leader fails. After this, as the operation is asynchronous and can proceed even if the current YB-Master leader fails, the table creation API returns a success.
Tablet assignments
The YB-Master component in YugabyteDB keeps track of all the tablets (data shards) and the YB-TServer nodes that are currently hosting them. It maintains a mapping of which tablets are stored on which YB-TServer nodes.
When clients, such as the YugabyteDB query layer or applications using the YCQL (Cassandra-compatible) or YSQL (PostgreSQL-compatible) APIs, need to retrieve data, they can efficiently query the YB-Master to get this tablet-to-node mapping. The smart clients then cache (store) this mapping locally.
By having the tablet-to-node mapping cached, the smart clients can communicate directly with the correct YB-TServer node that holds the required data, without needing to go through additional network hops or intermediate components. This direct communication allows for efficient data retrieval and query processing.
Load balancing
The YB-Master leader places (at CREATE TABLE time) the tablets across YB-TServers to enforce any user-defined data placement constraints and ensure uniform load. In addition, during the lifetime of the universe, as nodes are added, fail, or become decommissioned, it continues to balance the load and enforce data placement constraints automatically.
Leader balancing
Aside from ensuring that the number of tablets served by each YB-TServer is balanced across the universe, the YB-Masters also ensure that each node has a symmetric number of tablet leaders across nodes. This is also done for the followers.
Re-replication of data
The YB-Master receives regular "heartbeat" signals from all the YB-TServer nodes in the cluster. These heartbeats allow the YB-Master to monitor the liveness (active state) of each YB-TServer.
If the YB-Master detects that a YB-TServer has failed (stopped sending heartbeats), it keeps track of how long the node has been in a failed state. If this failure duration exceeds a predetermined threshold, the YB-Master initiates a process to replace the failed node.
Specifically, the YB-Master identifies replacement YB-TServer nodes and re-replicates (copies) the tablet data from the failed node to the new nodes. This re-replication process ensures that the data remains available and redundant, even after a node failure.
However, the YB-Master carefully throttles (limits) the rate of re-replication to avoid impacting the ongoing, regular operations of the database cluster. This throttling prevents the re-replication from overloading the system and affecting the performance of user queries and other foreground activities.
High availability
The YB-Master is not in the critical path of normal I/O operations, therefore its failure does not affect a functioning universe. Nevertheless, the YB-Master is a part of a Raft group with the peers running on different nodes. The number of peers is decided by the replication factor of the universe. One of these peers is the active master and the others are active standbys. If the active master (the YB-Master leader) fails, these peers detect the leader failure and re-elect a new YB-Master leader which becomes the active master in seconds of the failure.